启动到安全模式(Booting into Safe Mode)可以帮助您查明Windows计算机上的问题根源。如果有问题的 PC 组件在安全模式下(Safe Mode)运行顺畅,则意味着设备驱动程序错误、第三方应用程序漏洞百出、系统配置不正确、恶意软件或网络相关问题是问题的根本原因。
Windows具有三种不同的安全模式(Safe Mode)选项。本教程将向您展示如何以安全模式启动您的(Safe Mode)Windows 11 PC以及其选项有何不同。

1.从Windows 恢复环境(Windows Recovery Environment)进入安全模式(Enter Safe Mode)
如果您的 PC 未启动或未启动黑屏/空白屏幕,Windows恢复(Recovery)是在安全模式下启动(Safe Mode)Windows 11的最佳途径。
- 按住电源按钮,直到您的 PC 完全关闭。
- 等待(Wait)大约 10 秒钟,然后按电源按钮重新打开电脑。
- (Press)当您的 PC 屏幕亮起或屏幕上出现制造商的徽标时,按下电源按钮。按住电源按钮,直到您的 PC 关闭。
- 等待(Wait)大约 5-10 秒,然后按电源按钮打开电脑。
- 重复step #3步和step #4,您的 PC 应在第三次尝试时加载Windows 恢复环境(winRE)。(Windows Recovery Environment)
- 在恢复环境中选择疑难解答。(Troubleshoot)

- 选择高级选项(Advanced options)。

- 选择启动设置(Startup Settings)。

- 选择重新启动(Restart)以加载启动设置(Startup Settings)选项。

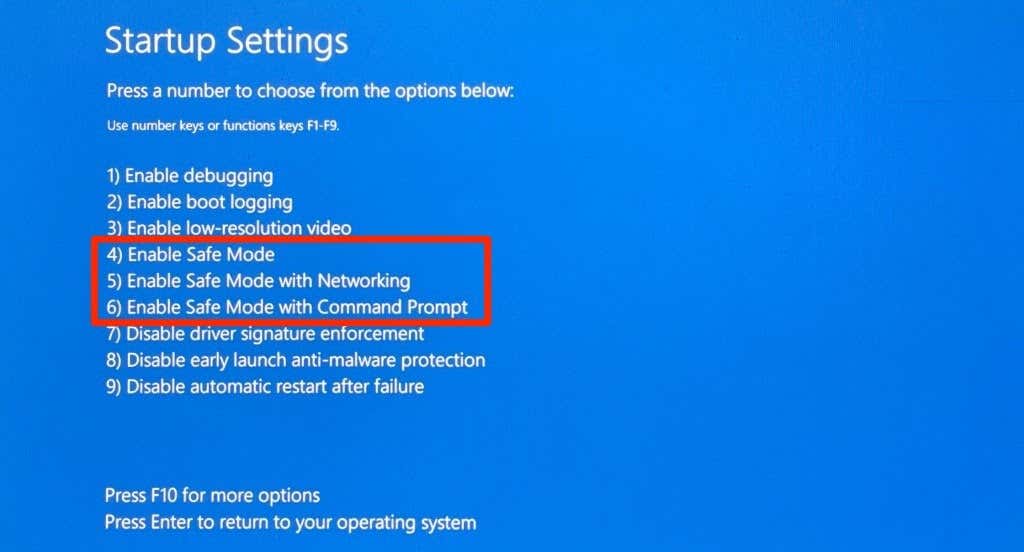
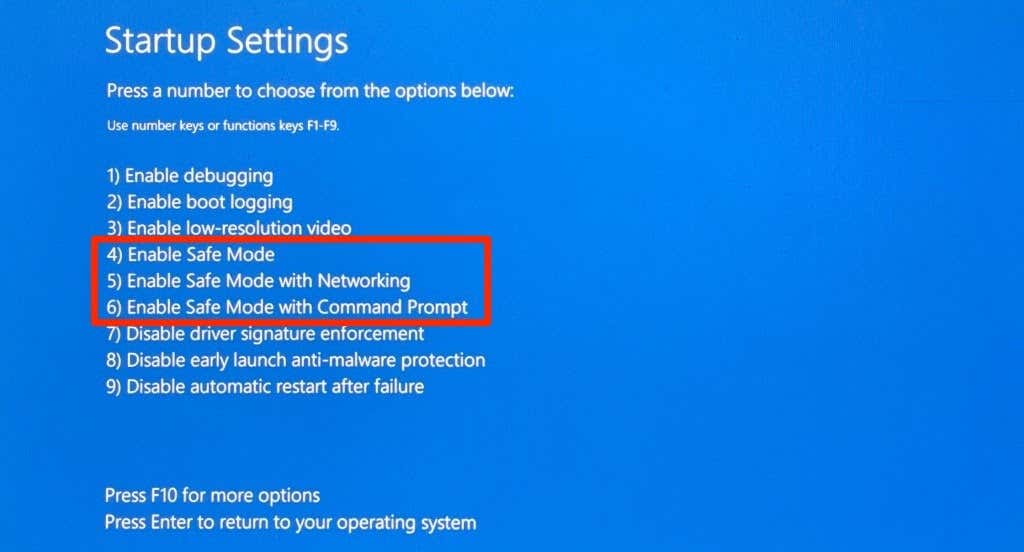
- 按(Press)要启动的安全模式(Safe Mode)选项旁边的相应数字。

- 按键盘上的4或F4启动进入常规安全模式(Mode)。此安全模式(Mode)选项会去除所有第三方应用程序和程序。“安全(Safe) 模式(Mode)”字样将出现在 PC 屏幕的四个角上。Windows将仅加载基本驱动程序和(Windows)设置(Settings)菜单中的几个选项。因此,您将无法使用 Internet 或对您的 PC 设置进行某些更改。

- 按5或F5以“启用(Enable Safe Mode)带网络连接的安全模式。(Networking.)” 此选项将加载您 PC 的网络驱动程序,让您在安全模式下(Safe Mode)访问互联网。仅当您要解决的问题与网络相关或需要访问 Internet 时,才应选择此选项。
- 按6或F6 启用“带命令提示符的(Command Prompt)安全模式(Safe Mode)”。与其他两个选项不同,此选项在屏幕上加载命令提示符终端。(Command Prompt)使用此选项进行可能需要运行CMD 命令(CMD commands)的高级故障排除。

如果您无法进入Windows 恢复环境(Windows Recovery Environment)并且您的计算机继续启动并进入空白屏幕,请考虑从可启动的USB驱动器启动Windows 11 。您可以使用 Microsoft 的媒体创建工具或下载Windows 11磁盘映像 ( ISO )在另一台Windows 11 PC 上创建可启动(Windows 11)USB驱动器。(USB)阅读我们关于创建 Windows 可启动 USB 恢复驱动器(creating a Windows bootable USB recovery drive)的教程以了解更多信息。
2.从 Windows 设置进入安全模式(Enter Safe Mode From Windows Settings)
与旧版Windows一样,您也可以从“设置”(Settings)应用进入Windows 11中的安全模式。(Safe Mode)
- 打开设置应用程序(按Windows 键(Windows key)+ I),在边栏中选择系统(System),然后选择恢复(Recovery)。

- 滚动到“恢复(Recovery)选项”部分,然后选择“高级启动”旁边的立即重新启动。(Restart now)
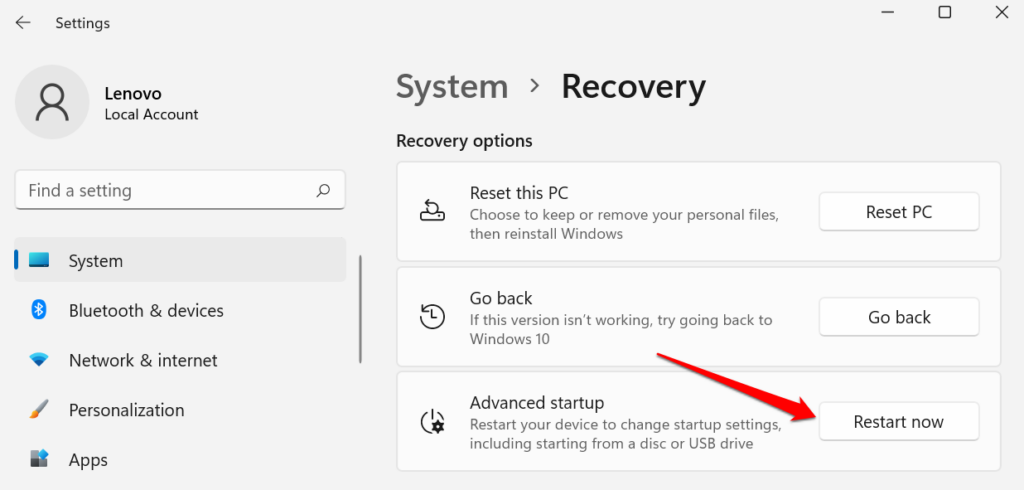
- 在确认提示上选择立即重新启动(Restart now)以继续。
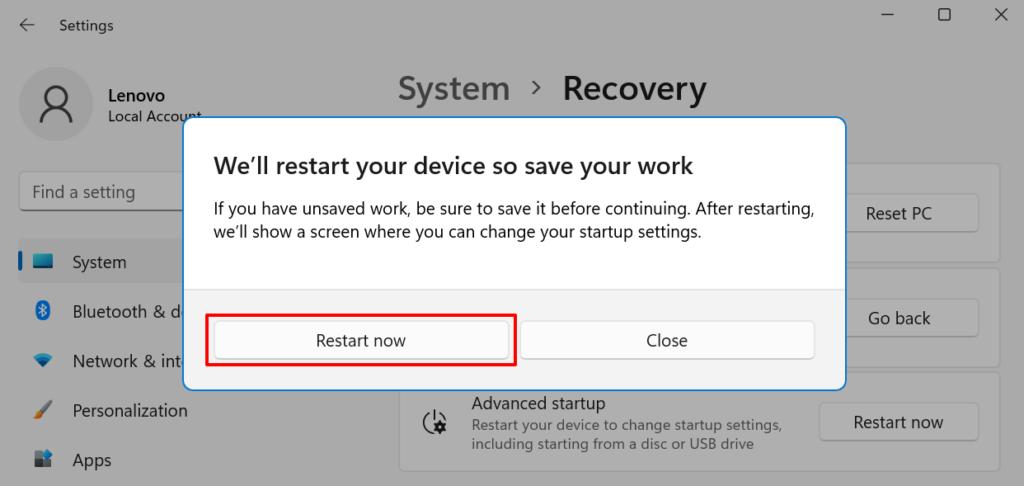
这会将您的 PC 引导至恢复环境。转到疑难解答(Troubleshoot)>高级选项(Advanced options)>启动设置(Startup Settings)>重新启动(Restart),然后按键盘上的4、5或6以启用您首选的安全模式(Mode)选项。
3.从开始菜单以安全(Start Menu)模式(Mode)启动(Start)Windows 11
使用开始菜单可能是将(Start Menu)Windows 11引导至安全模式(Mode)的最简单方法。通过在重新启动 PC 时按住 Shift键, (Shift)Windows将启动到高级启动菜单,您可以在其中进入安全模式(Mode)。
- 按Windows 键(Windows key)并选择电源图标(power icon)。
- 按住键盘上的Shift 键(Shift key)并选择重新启动(Restart)。
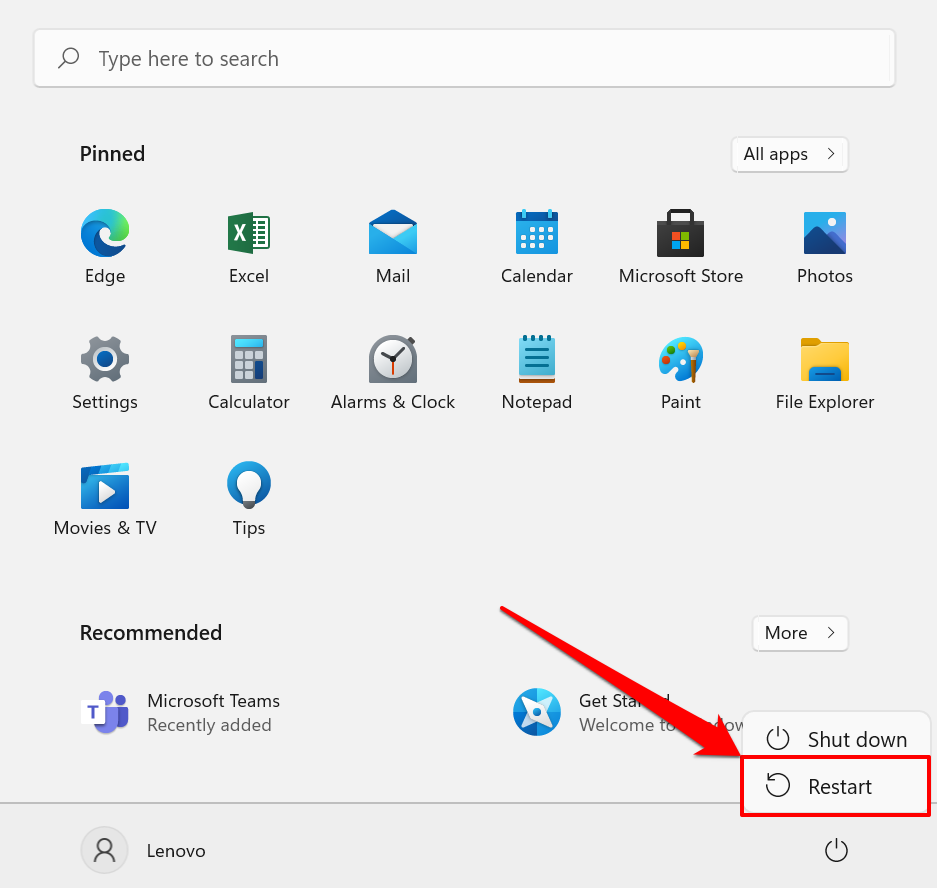
这将加载高级启动页面。然后,如上述方法所述,转到疑难解答(Troubleshoot)>高级选项(Advanced options)>启动设置(Startup Settings)>重新启动(Restart)并选择您喜欢的安全模式(Mode)类型。
4.使用 MSCONFIG 以安全模式(Mode Using MSCONFIG)启动(Start)Windows 11
MSCONFIG代表Microsoft 系统配置(Microsoft System Configuration)。它是一个内置的Windows工具,可让您访问在“(Windows)设置”(Settings)应用程序或“控制面板(Control Panel)”中可能找不到的系统设置。
- 按键盘上的Windows 键(Windows key)或选择任务栏中的搜索图标(Search icon)。

- 在搜索框中键入msconfig(又名System Configuration ),然后在结果窗格中选择Run as administrator 。

- 前往引导(Boot)选项卡并在“引导选项”部分检查安全引导(Safe boot)。

- 选择您喜欢的安全模式(Mode)选项:Minimal、Alternate shell、Active Directory repair或Network。
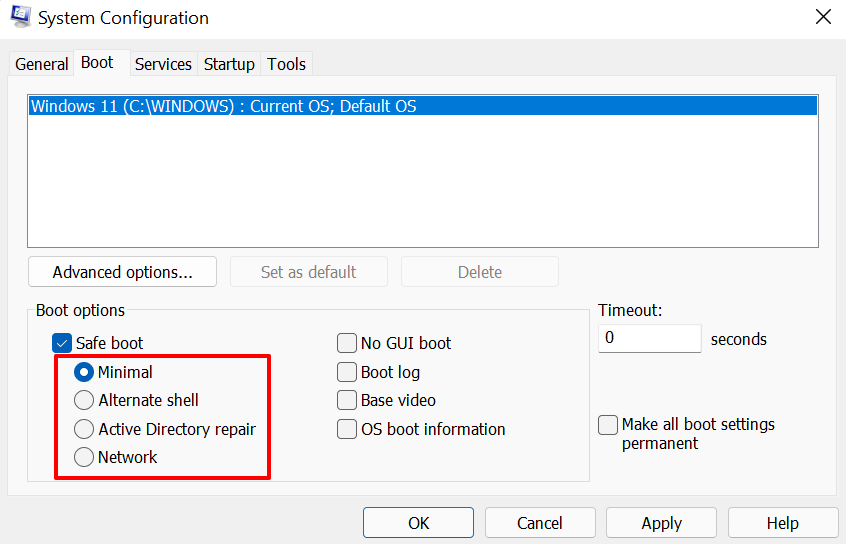
- “最小”选项将在安全模式下(Safe Mode)加载基本驱动程序和设置。但是,您将无法访问互联网、使用第三方应用程序以及修改某些系统配置。
- “备用(Alternate)外壳”将仅在安全模式下启动(Mode)命令提示符(Command Prompt)终端。
- “ Active Directory修复”通常由企业环境中的网络管理员用来修复或恢复 Active Directory 数据库(repair or restore an Active Directory database)。
- “网络”选项将以安全模式(Safe Mode)加载网络驱动程序。
- 选择应用(Apply),然后选择确定(OK)继续。

- 在出现提示时选择重新启动(Restart)以启动进入安全模式(Mode)。否则(Otherwise),请选择退出而不重新启动(Exit without restart)以稍后重新启动您的 PC,尤其是当您在其他应用程序中有未保存的文档时。

注意:(Note:)每次重新启动 PC 时,您的 PC 将始终启动到安全模式。(Mode)
以下步骤将禁用安全模式(Mode)并正常启动您的 PC:
返回“系统配置”窗口(单击(Click) 开始(Start),键入msconfig),取消选中安全启动(Safe boot),选择确定(OK),然后重新启动您的 PC 以禁用。

5.从命令提示符(Mode From Command Prompt)启用安全模式
将Windows 11(Windows 11)启动到安全模式(Mode)的另一种方法是通过命令提示符(Command Prompt)。
- 按Windows 键(Windows key),在搜索栏中键入命令提示符,然后选择(command prompt)以管理员身份运行(Run as administrator)。

- 在控制台命令提示符(Command Prompt)终端中键入或粘贴shutdown.exe /r /oEnter。

- 您将收到一条通知,通知您Windows将在不到一分钟的时间内关闭。选择关闭(Close)并等待您的 PC 启动进入Windows 恢复(Windows Recovery)页面。

- 在启动页面上,前往疑难解答(Troubleshoot)>高级选项(Advanced options)>启动设置(Startup Settings)>重新启动,然后按首选安全(Restart)模式(Mode)选项旁边的相应键。
6.从登录屏幕(Sign-in Screen)进入安全模式(Enter Safe Mode)
无需登录Windows也可以进入安全模式(Safe Mode)。选择登录屏幕左下角的电源图标,按住(power icon)Shift键,然后选择重新启动(Restart)。

您的 PC 将加载Windows 恢复环境(Windows Recovery Environment)。如以上部分所述,转到疑难解答(Troubleshoot)>高级选项(Advanced options)>启动设置(Startup Settings)>重新启动(Restart),然后选择安全模式选项。
安全模式还有更多功能
除了诊断性能和启动相关问题外,进入安全模式(Mode)还可以帮助诊断恶意软件感染(diagnose malware infections)和其他系统错误。
How to Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode
Booting into Safe Mode can help you pinpoint the source of a problem on your Windows computer. If a problematic PC component works smoothly in Safe Mode, that implies that bad device drivers, bug-ridden third-party apps, incorrect system configurations, malware, or network-related issues are the root cause of the problem.
Windows has three different Safe Mode options. This tutorial will show you how to start your Windows 11 PC in Safe Mode and how its options differ.

1. Enter Safe Mode from the Windows Recovery Environment
Windows Recovery is the best route to start Windows 11 in Safe Mode if your PC isn’t booting up or doesn’t boot past a black/blank screen.
- Hold the power button until your PC shuts down completely.
- Wait for about 10 seconds and press the power button to turn your PC back on.
- Press the power button when your PC’s screen lights up or when the manufacturer’s logo appears on the screen. Keep holding the power button until your PC shuts down.
- Wait for about 5-10 seconds and press the power button to turn on your PC.
- Repeat step #3 and step #4, and your PC should load the Windows Recovery Environment (winRE) on the third try.
- Select Troubleshoot in the recovery environment.

- Select Advanced options.

- Select Startup Settings.

- Select Restart to load the Startup Settings options.

- Press the corresponding number next to the Safe Mode option you want to boot.

- Press 4 or F4 on your keyboard to boot into regular Safe Mode. This Safe Mode option strips all third-party apps and programs. A “Safe Mode” inscription will appear in the four corners of your PC’s screen. Windows will only load basic drivers and few options in the Settings menu. Consequently, you won’t be able to use the internet or make certain changes to your PC settings.

- Press 5 or F5 to “Enable Safe Mode with Networking.” This option will load your PC’s network drivers, giving you access to the internet while in Safe Mode. You should only select this option if the problem you’re troubleshooting is network-related or requires access to the internet.
- Press 6 or F6 to enable “Safe Mode with Command Prompt.” Unlike the other two options, this option loads a Command Prompt terminal on the screen. Use this option for advanced troubleshooting where you might need to run CMD commands.

If you can’t enter the Windows Recovery Environment and your computer continues to boot into a blank screen, consider starting Windows 11 from a bootable USB drive. You can create a bootable USB drive on another Windows 11 PC using Microsoft’s media creation tool or by downloading Windows 11 disk image (ISO). Read our tutorial on creating a Windows bootable USB recovery drive to learn more.
2. Enter Safe Mode From Windows Settings
Like older Windows versions, you can also enter Safe Mode in Windows 11 from the Settings app.
- Open the Settings app (press Windows key + I), select System in the sidebar, and select Recovery.

- Scroll to the “Recovery options” section and select Restart now next to “Advanced startup.”

- Select Restart now on the confirmation prompt to continue.

That’ll boot your PC into the recovery environment. Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart and press either 4, 5, or 6 on your keyboard to enable your preferred Safe Mode option.
3. Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode From the Start Menu
Using the Start Menu is probably the easiest way to boot Windows 11 into Safe Mode. By holding the Shift key while restarting your PC, Windows will boot into the advanced startup menu, where you can enter Safe Mode.
- Press the Windows key and select the power icon.
- Press and hold the Shift key on your keyboard and select Restart.

That’ll load the advanced startup page. Then, as described in the method above, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart and select your preferred Safe Mode type.
4. Start Windows 11 in Safe Mode Using MSCONFIG
MSCONFIG stands for Microsoft System Configuration. It is a built-in Windows tool that lets you access system settings you may not find in the Settings app or Control Panel.
- Press the Windows key on the keyboard or select the Search icon in the taskbar.

- Type msconfig (aka System Configuration) in the search box and select Run as administrator in the result pane.

- Head to the Boot tab and check Safe boot in the “Boot options” section.

- Select your preferred Safe Mode option: Minimal, Alternate shell, Active Directory repair, or Network.

- The “Minimal” option will load basic drivers and settings in Safe Mode. However, you won’t be able to access the internet, use third-party apps, and modify certain system configurations.
- “Alternate shell” will boot only the Command Prompt terminal in Safe Mode.
- “Active Directory repair” is commonly used by network administrators in corporate environments to repair or restore an Active Directory database.
- The “Network” option will load the network drivers in Safe Mode.
- Select Apply and then select OK to proceed.

- Select Restart on the prompt to boot into Safe Mode. Otherwise, select Exit without restart to reboot your PC later, especially if you have unsaved documents in other apps.

Note: Your PC will always boot into Safe Mode each time you restart your PC.
The following steps will disable Safe Mode and boot your PC normally:
Return to the “System Configuration” window (Click Start, type msconfig), uncheck Safe boot, select OK, and reboot your PC to disable.

5. Enable Safe Mode From Command Prompt
Another way to boot Windows 11 into Safe Mode is via Command Prompt.
- Press the Windows key, type command prompt in the search bar, and select Run as administrator.

- Type or paste shutdown.exe /r /o in the console Command Prompt terminal and press Enter.

- You’ll get a notification that Windows will shut down in less than a minute. Select Close and wait for your PC to boot into the Windows Recovery page.

- On the startup page, head to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart and press the corresponding key next to your preferred Safe Mode option.

6. Enter Safe Mode from the Sign-in Screen
It’s also possible to enter Safe Mode without having to sign in to Windows. Select the power icon in the bottom-left corner of the sign-in screen, press and hold the Shift key, and select Restart.

Your PC will load the Windows Recovery Environment. As mentioned in the sections above, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart and select the Safe Mode option.

There’s More to Safe Mode
In addition to diagnosing performance and boot-related issues, entering Safe Mode can help diagnose malware infections and other system errors.

























