在您的 Windows 10 计算机上登录多个用户帐户可以加快它们之间的交换速度,但也会浪费资源,因为您的计算机被迫在内存中维护两个独立的环境。如果您希望有机会权衡此操作的收益与成本,任务管理器(Task Manager)可以提供帮助。您知道任务管理器(Task Manager)的哪个选项卡向您显示在线用户吗?它是“用户(Users)”选项卡:它可以让您查看哪些用户帐户已登录,还可以查看有多少计算机资源用于使它们保持在线状态。任务管理器(Task Manager)中的“用户(Users)”选项卡还允许您关闭其他用户打开的应用程序,甚至将它们注销。事不宜迟,让我们看看这是怎么一回事:
如何在Windows 任务管理器中查看用户选项卡(Windows Task Manager)
打开任务管理器(Task Manager)。最快的方法之一是同时按下键盘上的Ctrl + Shift + Esc键。如果它以仅列出您打开的应用程序的紧凑视图打开,请先单击或点击(click or tap)“更多详细信息”("More details")。
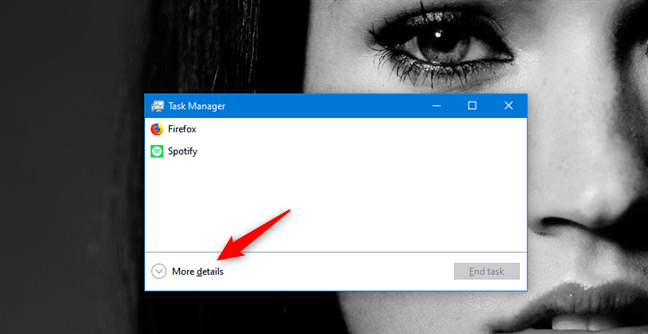
看到任务管理器(Task Manager)的完整版本后,选择用户(Users)选项卡。

在“用户(Users)”选项卡上,当前登录的用户帐户列在第一列中,然后是一些描述每个用户正在使用的系统资源的列。

默认情况下,您会看到用户(User)列附近显示六或七列。他们是:
-
状态(Status)- 显示列出的帐户和进程的状态。
-
CPU - 显示每个帐户使用的总 CPU 周期百分比,以及每个帐户运行的进程。
-
内存(Memory)- 显示所选帐户(或所选进程)正在使用的内存总量。
-
磁盘(Disk)- 指示传输到/从硬盘驱动器的数据量。
-
网络(Network)- 显示所选用户帐户或进程的网络使用情况。
-
GPU - 显示 PC 上所有图形芯片或卡的最高视频利用率。
-
GPU 引擎(GPU engine)- 如果您安装了多个显卡(例如在笔记本电脑上安装了专用显卡但在处理器上也有视频芯片),GPU 引擎(GPU engine)会显示专用显卡的利用率。
要添加其他列并显示更多信息,请右键单击(或点击并按住(tap and hold))列标题(column header)并选择其他条目。您的选择是:

您可以取消选择任何不需要关闭它的列。这有助于整理视图并保持窗口更小。
如何管理每个用户账户打开的进程(user account)
如果您具有管理权限,则可以从“用户”选项卡单击或点击每个(Users)用户帐户名称(user account name)旁边的小箭头,以展开该帐户打开的所有进程的列表。或者,您可以右键单击或长按帐户,然后单击(account and click)或点击展开。(Expand.)

如果您使用没有管理权限的标准用户帐户登录,您可以展开并仅查看您自己的进程列表。您看不到(If you are signed in with a standard user account that does not have administrative privileges, you can expand and see only your own list of processes. You cannot see the processes run by other users)连接到您的 Windows 10 PC 的其他用户运行的进程。
无论哪种方式,您都可以检查打开的进程列表以查找不需要运行的任何内容。如果您发现某个应用程序正在消耗资源并关闭它不会对帐户持有人(account holder)造成任何不必要的困难,您可以右键单击它(或按住(press and hold)),然后单击或点击(click or tap) “结束任务”。("End Task.")这将关闭该过程。

您也可以选择进程,然后单击(process and click)或点击屏幕右下角的“结束任务”按钮。("End Task")

完成帐户流程后,您可以再次点击箭头或右键单击或长按帐户并选择(account and select) 折叠(Collapse)以隐藏展开的列表并(list and display)再次仅显示名称。

如何在Windows 任务管理器中管理打开的用户帐户(Windows Task Manager)
如果您有多个未结账户,您可以执行各种任务来管理它们。首先(First),右键单击或按住帐户以查看可用选项。

从上下文菜单中选择连接(Connect)以切换到所选帐户。在提供的字段中输入帐户密码(account password),然后单击field and click/tap确定。(OK.)

如果要退出所选帐户(chosen account),请选择“退出”("Sign off")。如果您不需要打开它,这是释放资源的绝佳方式。请注意确保其他用户没有任何未保存的信息,因为这可能会导致数据丢失。如果您确定要注销该帐户,请单击(Click)或点击警告窗口(warning window)中的“注销用户” 。("Sign out user")

退出或切换到另一个帐户的另一种方法是选择该帐户,然后单击(account and click)或点击窗口右下角的相应按钮。

如果您想向其他帐户的用户发送消息,请从上述上下文菜单(context menu)中选择“发送消息” 。("Send message")在提供的空白处输入您的消息,如果需要,输入标题,然后单击或点击确定。(OK.)

如果远程用户正在积极使用所选帐户,他或她会立即收到您的消息。如果其他帐户的用户不在计算机上,他或她将在下次解锁该帐户时收到该消息。

最后,在右键菜单中,您可以选择“管理用户帐户”("Manage user accounts")以从旧的控制面板(Control Panel)中打开“用户帐户(User Accounts)”部分。

从那里,您可以更改帐户的设置。
您是否使用任务管理器(Task Manager)来管理登录用户?
任务管理器(Task Manager)中的“用户(Users)”选项卡没有很多功能,但它具有实际用途。只需稍加努力,您就可以查看所有未结帐户及其对系统性能的影响,并对其进行管理以重新获得资源。这比切换到另一个帐户以关闭程序并切换回来要快得多。有关在Windows中使用(Windows)任务管理器(Task Manager)的更多信息,请立即阅读以下推荐的文章。
How to manage signed-in user accounts with the Task Manager in Windows 10
Having multiple user accounts logged in on your Windows 10 computer can make swapping between them faster, but it can also waste resources as your computer is forced to maintain two separate environments in memory. If you want the chance to weigh the benefits of this action against the costs, the Task Manager can help. Do you know which tab of the Task Manager shows you the online users? It's the Users tab: it lets you view which user accounts are logged in and also see how much of the computer's resources are being used to keep them online. The Users tab from Task Manager also lets you close the apps opened by other users or even log them out. Without further ado, let's see what this is all about:
How to view the Users tab in the Windows Task Manager
Open the Task Manager. One of the fastest ways to do it is to simultaneously press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys on your keyboard. If it opens in its compact view, which only lists your open apps, click or tap on "More details" before anything else.

Once you see the full version of the Task Manager, select the Users tab.

On the Users tab, the user accounts currently logged in are listed in the first column, followed by some columns depicting system resources being used by each.

By default, you see six or seven columns displayed near the User column. They are:
-
Status - shows the status of the accounts and processes listed.
-
CPU - displays the percentage of total CPU cycles used by each account, and the processes run by each account.
-
Memory - shows the total amount of memory the selected account (or the chosen process) is utilizing.
-
Disk - indicates the amount of data being transferred to/from your hard drive.
-
Network - displays the network usage of the selected user account or process.
-
GPU - shows the highest video utilization across all the graphics chips or cards on your PC.
-
GPU engine - if you have more than one video card installed (like on a laptop with a dedicated video card but also a video chip found on the processor), GPU engine shows the utilization of the dedicated graphics card.
To add additional columns and display more information, right-click (or tap and hold) a column header and select other entries. Your options are:
-
ID - shows the unique session ID for each account.
-
Session - displays the type of session for each account. This is only useful for a server system where users may log in using remote services.
-
Client Name - displays the name of the computer a remote user is logging in from.

You can deselect any column you do not need to close it. This helps declutter the view and keep the window smaller.
How to manage the processes opened by each user account
If you have administrative rights, from the Users tab, you can click or tap the small arrow next to each user account name to expand a list of all processes opened by that account. Alternatively, you can right-click or long-press an account and click or tap Expand.

If you are signed in with a standard user account that does not have administrative privileges, you can expand and see only your own list of processes. You cannot see the processes run by other users that are connected to your Windows 10 PC.
Either way, you can check the list of open processes for anything that does not need to be running. If you find an application that is chewing up resources and closing it would not cause any undue hardship on the part of the account holder, you can right-click on it (or press and hold) and click or tap "End Task." This closes the process.

You can also select the process and click or tap the "End Task" button on the lower-right corner of the screen.

Once you have gone through the account's processes, you can tap the arrow once again or right-click or long-press the account and select Collapse to hide the expanded list and display only the name once again.

How to manage open user accounts in the Windows Task Manager
If you have multiple open accounts, there are various tasks you can perform to manage them. First, right-click or press-and-hold the account to view the options available.

Select Connect from the contextual menu to switch to the selected account. Enter the account password in the provided field and click/tap on OK.

Select "Sign off" if you want to sign out the chosen account. If you do not need it open, this is an excellent way to free up resources. Be careful to ensure that the other user does not have any unsaved information as this could result in data loss. Click or tap "Sign out user" from the warning window if you are confident that you want to log out that account.

Another way to sign out of or switch to another account is to select the account and click or tap the appropriate button on the lower-right corner of the window.

Select "Send message" from the context menu described above if you want to send a message to the user of the other account. Type your message in the space provided, enter a title if you wish and then click or tap OK.

If a remote user is actively using the selected account, he or she gets your message immediately. If the user of the other account is not on the computer, he or she will get the message the next time he or she unlocks the account.

Finally, in the right-click menu, you can select "Manage user accounts" to open the User Accounts section from the old Control Panel.

From there, you can change the account's settings.
Do you use the Task Manager to manage signed in users?
The Users tab in the Task Manager does not have a ton of features, but it serves a practical purpose. With a little effort, you can view all open accounts, their impact on your system's performance and manage them to regain resources. It is much faster than swapping over to another account to close a program and switching back. For more information about utilizing the Task Manager in Windows, do not hesitate to read the articles recommended below.















