您是否听说过性能监视器(Performance Monitor),也称为PerfMon.exe或PerfMon.msc?它是一个复杂的工具,可用于监控您的Windows 计算机或设备(Windows computer or device)的性能。使用它,您可以看到您的计算机如何管理其资源。它为您提供的信息可以帮助您做出有关软件和硬件选择(software and hardware choices)的决定,尤其是当您的计算机性能低于预期时。当您想要进行一些故障排除时,它也很有用。以下是如何使用性能监视器(Performance Monitor)像专业人士一样分析系统性能:
注意:(NOTE:)本指南适用于Windows 10、Windows 7 和Windows 8.1。
如何在Windows中启动(Windows)性能监视器(Performance Monitor)
启动性能监视器(Performance Monitor)的方法有很多。适用于所有Windows版本的一种方法是使用搜索。例如,在Windows 10中,在任务栏的搜索框中(search box)键入“性能监视器”("performance monitor"),然后单击或点击相应的结果。

有关在任何Windows 版本(Windows version)中打开性能监视器(Performance Monitor)的其他方法,请查看这篇文章:在Windows(所有版本)中启动性能监视器的 11 种方法。(Performance Monitor)
如何使用性能监视器分析(Performance Monitor)系统性能(system performance)
要开始分析计算机的当前性能,请单击或点击(click or tap)程序主面板上监视工具(Monitoring Tools)下的性能监视器(Performance Monitor),如下所示。

注意:(NOTE:)如果您想查看您的计算机在使用一组特定应用程序和程序(apps and programs)时的性能,请务必立即打开它们,以便图表可以记录它们对系统资源的影响。
默认情况下,性能监视器(Performance Monitor)显示的图表测量处理器(Processor)时间,这是处理器忙于运行活动程序的时间量(以百分比显示)。这为您提供了处理器工作强度的基本衡量标准。

可以使用其他列和其他几个选项自定义此图。要进行更深入的分析,您还可以将计数器添加到可以详细说明其他数据的图表中。为此,请点击图表上方的绿色加号。

在打开的添加计数器(Add Counters)窗口中,您可以选择要实时监控的计数器。它们按类型组织,数量众多。如果双击(双击)计数器的名称,您应该会看到几个单独的对象,并且您可以选择监视其中的任何一个以及所有这些对象。
选择完要监视的计数器和对象后,单击或点击添加(Add)按钮。添加的计数器显示在窗口的右侧。当您单击或点击确定(OK)时,它们会从性能监视器(Performance Monitor)添加到图表中。

例如,在下图中,我们使用了处理器(Processor) 计数器集(counter set)。它显示了技术性但有用的数据,例如Interrupts/sec(要求您的处理器响应的中断数。它们由硬盘控制器(disk controller)适配器和网络接口(network interface)卡等硬件组件生成)或% (total amount)%User Time(非- 用于用户模式操作的空闲时间)。

现在,您可以使用选定的计数器继续执行您想要监控的活动,并查看它们如何实时变化。
如何自定义数据在性能监视器中的显示方式(Performance Monitor)
您还可以通过单击或点击“更改图表类型”("Change graph type")按钮(或按键盘上的CTRL + G)并选择直方图栏(Histogram bar)或报告(Report)选项来查看其他格式的数据。

此图以直方图(Histogram)格式显示数据。

这里我们有一个报告(Report)选项的数据显示示例。
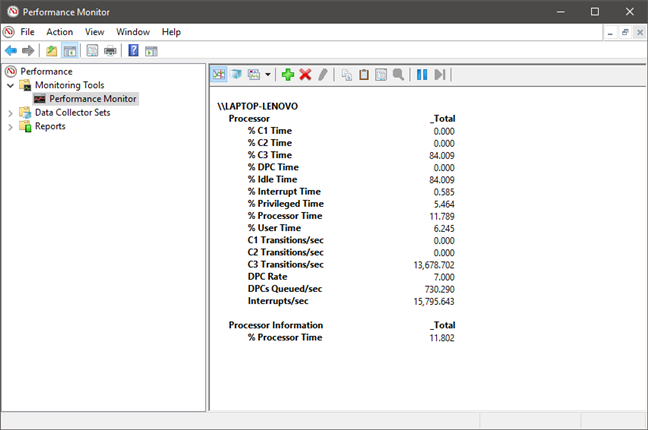
您可以通过单击下面突出显示的“属性(Properties)”按钮或按键盘上的CTRL + Q来进一步更改数据的显示方式。

这将打开“性能监视器属性(Performance Monitor Properties)”窗口,您可以在其中自定义每个计数器的显示方式、颜色、使用的线条类型等。您可以将数据(Data)和图表(Graph)选项卡用于此类个性化。
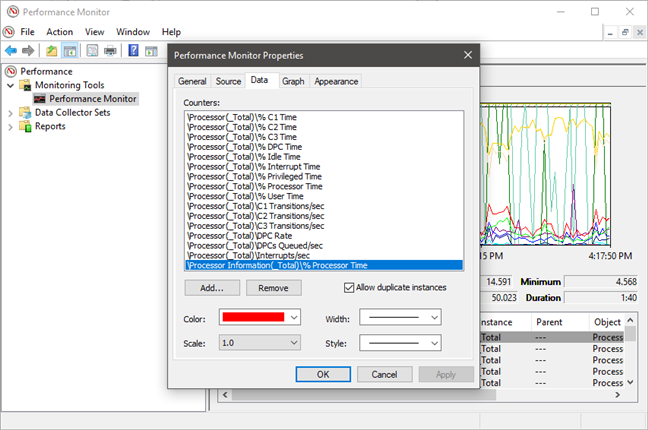
当您按照自己的意愿完成个性化设置后,不要忘记按下OK按钮。
哪些是最有用的性能监视器(Performance Monitor)计数器?
性能监视器(Performance Monitor)的图形报告中包含的数据技术含量高,普通用户难以理解。但是,有一些计数器比其他计数器更有用,至少对于办公桌上装有Windows 计算机的普通用户来说是这样。(Windows computer)以下是一些性能计数器,可以帮助您查看是否有问题:
-
Processor -> % Processor Time:您可以在计数器的处理器(Processor)列表中找到它。它向您显示处理器在各种任务上花费的时间。如果它的值一直在 80% 以上,则意味着你的处理器不够强大,无法支持你在计算机上所做的一切,因此它成为了瓶颈。尽管解决此问题的方法是在您的计算机上使用要求不高的应用程序,但唯一的长期解决方案是升级您的处理器。
-
Memory -> Available MBytes:可在计数器的内存(Memory)列表中找到。您可以将此计数器添加到图表中,以查看您的系统是否有足够的内存可供使用。如果图表显示可用内存不到总容量的 10%,则可能意味着您没有安装足够的RAM。在这种情况下,请考虑添加更多。
-
PhysicalDisk -> Current Disk Queue Length和PhysicalDisk -> % Disk Time:这两个计数器都在PhysicalDisk列表中。如果Current Disk Queue Length大于 2 并且Disk Time接近100%,则可能是您正在观看的硬盘驱动器太慢甚至出现故障。在这种情况下,您可能需要考虑升级硬盘驱动器。

如何理解性能监视器中可用的所有数据(Performance Monitor)
不幸的是,性能监视器(Performance Monitor)中可用的计数器列表非常长,我们无法在一篇文章中涵盖所有内容。但是,如果您正在寻找一个好的知识库(knowledge base),解释所有诸如%DPC Time或Page Faults/secMicrosoft的 TechNet上的此条目: Performance Monitor Counters。在那里,您将找到有关标准报告列表中的每个计数器的完整信息。
您是否使用性能监视器(Performance Monitor)来查找系统中的瓶颈?
本文向您展示了如何打开并获得对性能监视器(Performance Monitor)报告的基本阅读,以及如何应用计数器集来进一步监视系统的活动。我们还展示了一些有用的计数器,它们可以帮助您对Windows 计算机(Windows computer)中的主要硬件部件进行分析。您(Did)是否使用性能监视器(Performance Monitor)对 PC 进行故障排除?让我们知道您如何使用此工具以及它是否对您的目的有所帮助。
How to work with the Performance Monitor in Windows
Have you heard about the Performance Monitor, also known as PerfMon.exe or PerfMon.msc? It is a sophisticated tool that can be used to monitor the performance of your Windows computer or device. Using it, you can see how your computer manages its resources. The information it gives you can help you make decisions about software and hardware choices, especially when your computer's performance is below expectations. It is also useful when you want to do some troubleshooting. Here is how to use the Performance Monitor to analyze your system's performance like a pro:
NOTE: This guide works in Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
How to start the Performance Monitor in Windows
The are many ways to start the Performance Monitor. One that works in all versions of Windows is to use the search. For example, in Windows 10, type "performance monitor" in the search box on the taskbar and then click or tap the appropriate result.

For other ways to open the Performance Monitor in any Windows version, check this article: 11 ways to start Performance Monitor in Windows (all versions).
How to analyze system performance with Performance Monitor
To begin an analysis of your computer's current performance, click or tap on Performance Monitor under Monitoring Tools on the program's main panel, as indicated below.

NOTE: If you want to see how your computer performs while using a particular set of apps and programs, make sure to open them now so that the graphs can take note of their impact on your system's resources.
By default, the graph shown by Performance Monitor measures Processor time, which is the amount of time that the processor is busy working on running active programs (shown in percentages). This gives you a basic measure of how hard your processor is working.

This graph can be customized with additional columns and several other options. For a more in-depth analysis, you can also add counters to the graph that can detail other data. To do this, hit the green plus sign above the graph.

In the Add Counters window that opens, you can select the counters that you want to monitor in real time. They are organized by type and they are many. If you double-click (double-tap) on the name of a counter, you should see several individual objects and you can select to monitor any of them, as well as all of them.
When you are done selecting the counters and the objects that you want to monitor, click or tap the Add button. The added counters are shown on the right side of the window. When you click or tap OK, they are added to the graph from the Performance Monitor.

For example, in the graph below, we used the Processor counter set. It shows technical but useful data such as Interrupts/sec (the numbers of interrupts your processor was asked to respond to. They are generated by hardware components like hard disk controller adapters and network interface cards) or %User Time (the total amount of non-idle time that was spent on user mode operations).

Now you can go ahead and perform the activities that you want to be monitored, using the selected counters and see how they change in real time.
How to customize the way data is displayed in Performance Monitor
You can also look at the data in other formats by clicking or tapping on the "Change graph type" button (or by hitting CTRL + G on your keyboard) and choosing the Histogram bar or Report options.

This picture shows the data in Histogram format.

And here we have an example of the data display for the Report option.

You can further change how the data is displayed, by clicking the Properties button highlighted below or by pressing CTRL + Q on your keyboard.

This opens the Performance Monitor Properties window, where you can customize how each counter is displayed, in what color, using which type of lines and so on. You can use both the Data and the Graph tabs for this type of personalization.

When you are done personalizing everything as you wish, do not forget to press the OK button.
Which are the most useful Performance Monitor counters?
The data included in the Performance Monitor's graphical reports are highly technical and difficult to understand by casual users. However, there are a few counters that are more useful than others, at least for the regular user with a Windows computer in his or her desk. Here is a selection of performance counters that can help you see whether something is not working right:
-
Processor -> % Processor Time: you can find it in the Processor list of counters. It shows you the time spent by the processor on various tasks. If its value is consistently above 80%, it means that your processor is not powerful enough to sustain everything you do on your computer, so it becomes a bottleneck. Although a solution to this issue would be to use less demanding apps on your computer, the only long-term solution is to upgrade your processor.
-
Memory -> Available MBytes: is found in the Memory list of counters. You can add this counter to your graph to see whether your system has enough memory available to use. If the graph shows you that the available memory is somewhere less than 10 percent of your total amount, it could mean that you do not have enough RAM installed. In that case, consider adding some more.
-
PhysicalDisk -> Current Disk Queue Length and PhysicalDisk -> % Disk Time: these two counters are found both in the PhysicalDisk list. If the Current Disk Queue Length is higher than 2 and the Disk Time is closing on 100%, it is likely that the hard drive that you are watching is too slow or even faulty. In that case, you might want to consider upgrading your hard drive.

How to make sense of all the data that is available in Performance Monitor
Unfortunately, the list of counters available in Performance Monitor is exceptionally long and we cannot cover everything in just one article. However, if you are looking for a good knowledge base, explaining all the gibberish terms like %DPC Time or Page Faults/sec, read this entry on Microsoft's TechNet: Performance Monitor Counters. There you will find complete information about each counter found in the standard list of reports.
Do you use the Performance Monitor to find the bottlenecks in your system?
This article has shown you how to open and get an essential reading of Performance Monitor reports and how to apply counter sets to monitor the activity of your system further. We have also shown a few useful counters that can help you perform an analysis of the main hardware parts in your Windows computer. Did you use the Performance Monitor for troubleshooting your PC? Let us know how you use this tool and whether it was helpful for your purposes.












