为了使所有 PC 保持同步,更新互联网时间将帮助您完成它。为此,您需要先找到NTP(网络时间协议(Network Time Protocol))服务器。
Windows 的命令提示符(Command Prompt )将带您到那里。如果您不知道从哪里开始,请不要担心。
在这篇文章中,您将了解如何查找域的NTP服务器所需的知识。

注册并开始
如果您还没有注册Windows 时间服务(Windows Time Service),下面的命令将向您展示如何注册。您还需要启动该服务,然后才能将您的计算机时间与您的NTP服务器同步。
首先是启动命令提示符(Command Prompt)。选择以管理员身份运行(Run as administrator)。

然后输入以下命令注册您的系统:w32tm
/register

一旦你点击进入,你会发现注册是否成功。

现在,通过发出以下命令启动:sc start w32time

W32tm /查询
现在
Windows 时间服务(Windows Time Service)已注册并正在运行,您可以从中获取信息。您可以通过键入以下内容来执行此操作:w32tm /query 并将其与以下参数匹配。
/地位
这将显示Windows 时间服务(Windows Time Service)的状态。

/状态 /详细
这将设置详细模式以向您显示更多信息。

/来源
这将向您显示时间源。

/配置
这将显示运行时的配置和设置。

/同行
这将显示使用您的系统的人员列表。

W32tm /重新同步
您还可以使用命令提示符(Command Prompt )尽快重新同步时钟。
以下是对该命令的每个参数的讨论:
/computer:<要重新同步的计算机名称>
这使您可以指定将重新同步的计算机。如果将此留空,则主题将是本地计算机。
/等待
这使您可以消除重新同步的等待时间。这意味着您不必在返回结果之前等待该过程完成。
/柔软的
这使您可以使用现有错误重新同步时钟。当然,这对你没有任何好处。但是您可以参考它提供的信息以了解兼容性。

W32tm /配置
使用此命令配置您的系统。
让我们看看它的组成部分:
/manualpeerlist:
这使您可以设置对等点列表。这是一个IP地址列表。
您可以将其留空,默认情况下,它将设置为 <peers>。
/更新
这允许您通知服务有新的更改需要生效。
/localclockdispersion:<以秒为单位>
这配置了内部(Internal)时钟的精度。
/可靠:<是或否>
这允许您指定系统是否是可靠的时间来源。
/largephaseoffset:<以毫秒为单位>
这使您可以设置涉及本地时间和网络时间的时差。

W32tm /dumpreg
要获取有关注册表项的信息,您还可以转到命令提示符(Command Prompt)。在那里,输入以下内容以及w32tm /dumpreg
/子键:<键>
这将向您显示与默认键的子键关联的值。
/computer:<计算机名称>
这将向您显示指定计算机的查询注册表设置。

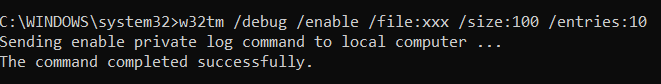
W32tm /调试
命令提示符(Command Prompt )也是您可以访问计算机私人日志的地方。以下是该类别中参数的简短讨论。
/启用或/禁用
这使您可以启用(enable )或禁用(disable )私人日志。因为您要访问此日志,所以启用是要走的路。
/file:<你的文件名>
这使您可以指定文件的名称。在下面的示例中,假设我们的文件名为“xxx”。
/size:<文件大小>
这使您可以指定文件的大小。您应该在此处输入最大字节数。在示例中,我们的文件大小为 100 字节。
/条目:<条目数>
这允许您列出条目的值。此字段的有效数字介于 0 到 300 之间。在示例中,值为 10。
How to Find NTP Server in a Domain to Sync All PCs
To kеep all PCs
synchronіzed, updating the internet time will help you pull it off. And to do
that, you need to fіnd thе NTP (Network Time Protocol) serνer first.
Windows’ Command Prompt will get you there. And
if you don’t know where to begin, don’t worry.
In this post,
you’ll learn what you need on how to find the NTP server for the domain.

Register and Start
If you haven’t
registered Windows Time Service yet, the commands below will show you how to do
it. You also need to start the service before you can sync your computer time
with your NTP server.
First up is to
launch the Command Prompt. Choose Run as administrator.

Then enter the
following command to register your system: w32tm
/register

Once you hit
enter, you will find out if the registration was a success.

Now, start things
up by issuing this command: sc start
w32time

W32tm /query
Now that the
Windows Time Service is registered and running, you can get information from
it. You can do this by typing the following: w32tm /query and match it with the following parameters.
/status
This will show
you the status of Windows Time Service.

/status
/verbose
This will set the
verbose mode to show you more information.

/source
This will show
you the time source.

/configuration
This will show
you the run-time’s configuration and settings.

/peers
This will show a
list of people using your system.

W32tm
/resync
You can also use
the Command Prompt to resynchronize
the clock the soonest time possible.
Here’s a
discussion on each parameter of this command:
/computer:<name
of computer to be resynchronized>
This lets you
specify a computer that will be resynchronized. If you leave this blank, the
subject will be the local computer.
/nowait
This lets you
eliminate the wait time for the resynchronization. It means that you will not
have to wait for the process to be completed before the results are returned.
/soft
This lets you
resync the clock using the existing errors. Of course, this wouldn’t do you any
good. But you can refer to the information it provides for compatibility.

W32tm
/config
Use this command
to configure your system.
Let’s look at its
components:
/manualpeerlist:
This lets you set
a list of peers. It’s a list of IP addresses.
You can leave it
blank and by default, it will be set to <peers>.
/update
This allows you
to notify the service that there are new changes that need to take effect.
/localclockdispersion:<in
seconds>
This configures
the Internal clock’s accuracy.
/reliable:<YES
or NO>
This allows you
to specify whether the system is a reliable source for time.
/largephaseoffset:<in
milliseconds>
This lets you set
the time difference involving your local and network time.

W32tm
/dumpreg
To get
information about a registry key, you can also go to the Command Prompt. There, enter the following, along with w32tm /dumpreg
/subkey:<key>
This shows you
the values that are associated with the sub-key of the default key.
/computer:<name
of the computer>
This shows you
the queries registry settings for a specified computer.

W32tm
/debug
The Command Prompt is also where you can
access your computer’s private log. Here’s a short discussion of the parameters
in this category.
/enable
or /disable
This lets you enable or disable the private log. Because you want to access this log,
enabling is the way to go.
/file:<name
of your file>
This lets you
specify the name of your file. In the example below, let’s say the name of our
file is “xxx”.
/size:<size
of your file>
This lets you
specify the size of your file. What you should enter here is the maximum number
of bytes.in the example, the size of our file is 100 bytes.
/entries:<number
of entries>
This allows you
to list down the value for your entries. The valid numbers for this field are
in between 0 to 300. In the example, the value is 10.















