从Windows Vista开始,Microsoft在其Windows操作系统中包含Windows Experience Index 。根据微软(Microsoft)的说法,“ Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)衡量您的计算机硬件和软件配置的能力,并将此衡量标准表示为一个称为基本分数的数字”。想知道这究竟意味着什么?本文将解释Windows如何计算Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)分数及其与您的计算体验的相关性。
什么是Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)?
Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)是Microsoft对计算机运行Windows性能的衡量标准,虽然它可能有用,但它有一定的迟钝。
Microsoft将(Microsoft)基本得分(base score)为 2.0的计算机定义为能够运行一般计算任务的计算机,但它的功能不足以在Windows 7或Windows 8中运行Aero或高级多媒体功能。基本得分(base score)为3.0 可以在基本级别上运行Aero和许多Windows功能,但在运行更高级别的功能时可能会出现问题,例如播放HDTV 内容(HDTV content)或以更高分辨率显示主题。
运行Windows 7(Windows 7)的主流计算机的分数至少应为 4。由于同时发生的技术进步,运行Windows 8的计算机的分数应高于 5。(Windows 8)7 分及以上的分数通常意味着更高端的计算机(end computer),例如功能强大的工作站或游戏机。
Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)定义中令人困惑且关键的部分是“基本分数(base score)”。Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)不是子分数的平均值。相反,Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)只是您的计算机获得的最低分数。就好像学校的成绩单(report card)只列出了最低成绩,所以英语(English)的“C”盖过了数学和科学(Math and Science)的“A” 。
如果不完全理解,这可能会产生误导,因为即使新笔记本电脑拥有所有最新组件,它也可能只会获得中等分数。(middling score)但是,如果笔记本电脑包含基本的英特尔(Intel)图形芯片,而不是来自Nvidia 或 AMD(Nvidia or AMD)的芯片,则该组件将是Windows显示的分数,尽管它有 12GB 的RAM和四核CPU。
如何查看您的Windows 体验指数分数(Windows Experience Index Score)
要查看计算机在Windows 7和Windows 8中的(Windows 8)Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)分数,请打开控制面板(Control Panel)中的性能信息和工具(Performance Information and Tools)。如果您使用的是 Classic View,它有一个直接的快捷方式。

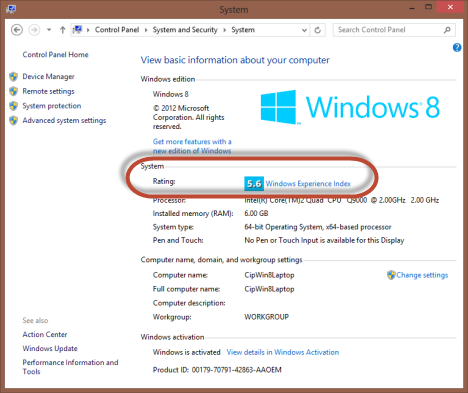
另一种方法是打开控制面板(Control Panel)并转到System and Security -> System。在“系统(System)”部分中,单击或点击“评级 - Windows 体验指数”("Rating - Windows Experience Index")链接。
您也可以使用搜索。在 Windows 7 的开始菜单(Start Menu)搜索框中(search box)或直接在Windows 8的开始(Start)菜单中输入单词体验(experience)。在 Windows 7 中,单击“检查 Windows 体验索引”("Check the Windows Experience Index")链接。在Windows 8中,按设置过滤,然后单击或点击(click or tap)“使用工具提高性能”("Use tools to improve performance")。

当您打开“性能信息和工具”("Performance Information and Tools")窗口时,它会在右侧显示Windows 体验指数基本分数。(Windows Experience Index)
在解释结果之前,让我们看看基本分数(base score)和其他分数是如何计算的。
如何计算 Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index Is Calculated)
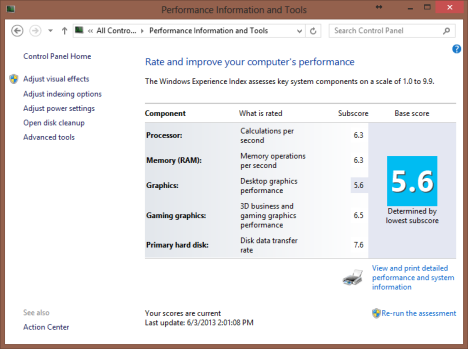
为了计算计算机的Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)分数,Windows会对某些组件进行评分并给它们一个子分数。这些组件由以下区域定义:
-
处理器(Processor)- 每秒计算;
-
内存 (RAM)(Memory (RAM)) - 每秒内存操作;
-
图形(Graphics)- Windows 7 中 Aero 等 Windows 功能的桌面图形性能;
-
游戏图形(Gaming graphics)- 3D 商业和游戏图形性能;
-
主硬盘(Primary hard disk)- 安装操作系统的硬盘的磁盘数据传输速率。

在Windows 7(Windows 7)中检查这些组件并给出介于 1.0 到 7.9 之间的分数。Windows 8 将分数范围扩大(score range)到 9.9,以反映最近的技术进步。得分最低的组件是Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)得分。
如何重新计算您的Windows 体验指数分数(Windows Experience Index Score)
如果升级了上述组件之一,则可以通过返回性能信息工具(Performance Information Tools)窗口并单击(window and clicking)或点击窗口右下方的“重新运行评估”链接来重新计算("Re-run the assessment")Windows 体验指数分数。(Windows Experience Index)

建议您在运行此重新评估之前退出所有打开的应用程序。单击或点击链接后,屏幕可能会闪烁,并显示与下图类似的对话框(dialog box)。

请注意,重新评估需要几分钟,因此请准备好等待。
结论:不要出汗
关于Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index),要记住的最重要的事情是不要挂断它。尽管它可以提供信息,但它似乎主要用于Microsoft获取有关运行Windows的硬件的数据。因此,仅仅因为机器上的分数处于中低端,并不意味着应该升级“最低”组件。也不应该有人寻找具有最高Windows 体验指数(Windows Experience Index)的计算机来购买。
The Windows Experience Index - How to Use it & Interpret the Results
Starting with Windows Vista, Microsoft includes the Windows Experience Index in its Windows operating systems. According to Microsoft, "the Windows Experience Index measures the capability of your computer's hardware and software configuration and expresses this measurement as a number called a base score". Wonder what that really means? This article will explain how Windows calculates the Windows Experience Index score and its correlation to your computing experience.
What is the Windows Experience Index?
The Windows Experience Index is Microsoft's measurement of how well a computer can run Windows and, although it can be useful, there is a certain obtuseness about it.
Microsoft defines a computer with a base score of 2.0 as one that has the ability to run general computing tasks, but it would not be powerful enough to run Aero or advanced multimedia features in Windows 7 or Windows 8. A computer with a base score of 3.0 can run Aero and many of Windows's features at a basic level, but it might have issues running higher level functions, such as playing HDTV content or displaying themes at higher resolutions.
Mainstream computers running Windows 7 should have a score of at least 4. Computers running Windows 8 should have a score above 5, due to the advances in technology that have happened in the meantime. A score of 7 and above generally means a higher end computer, such as powerful workstations or gaming machines.
The confusing - and key - part of Windows Experience Index's definition is the "base score". The Windows Experience Index isn't an average of the subscores. Rather, the Windows Experience Index is only the lowest subscore your computer earns. It is as if the report card from school only lists the lowest grade achieved, so that 'C' earned in English overshadows the 'A' earned in Math and Science.
If not fully understood, this can be misleading because a new laptop might only receive a middling score even though it has all the newest components. However, if a laptop contains a basic Intel graphics chip instead of a chip from Nvidia or AMD, that component will be the score Windows displays, despite its 12GB of RAM and its quad-core CPU.
How to View Your Windows Experience Index Score
To view a computer's Windows Experience Index score in Windows 7 and Windows 8, open Performance Information and Tools in the Control Panel. If you are using the Classic View, it has a direct shortcut.

An alternative is to open the Control Panel and go to System and Security -> System. In the System section, click or tap the "Rating - Windows Experience Index" link.

You can also use search. Type the word experience in Windows 7's Start Menu search box or directly in Windows 8's Start menu. In Windows 7, click on the "Check the Windows Experience Index" link. In Windows 8, filter by settings and click or tap "Use tools to improve performance".

When you open the "Performance Information and Tools" window, it displays the Windows Experience Index base score, on the right.

Before you interpret the results, let's see how the base score and other scores are calculated.
How the Windows Experience Index Is Calculated
To calculate a computer's Windows Experience Index score, Windows rates certain components and gives them a subscore. Those components are defined by the following areas:
-
Processor - Calculations per second;
-
Memory (RAM) - Memory operations per second;
-
Graphics - Desktop graphics performance for Windows features like Aero, in Windows 7;
-
Gaming graphics - 3D business and gaming graphics performance;
-
Primary hard disk - Disk data transfer rate for the hard disk where the operating system is installed.

These components are examined and given a score between a range of 1.0 to 7.9 in Windows 7. Windows 8 extends the score range to 9.9, to reflect the recent advances in technology. The component with the lowest score is the Windows Experience Index Score.
How to Recalculate Your Windows Experience Index Score
If one of the aforementioned components are upgraded, the Windows Experience Index score can be recalculated by returning to Performance Information Tools window and clicking or tapping the "Re-run the assessment" link found on the lower right-side of the window.

It is recommended that you exit all open applications before running this reassessment. Once you click or tap the link, the screen might flash and a similar dialog box to the one below is shown.

Note that the reassessment takes a few minutes so be prepared to wait.
Conclusion: Don't Sweat It
The most important thing to remember about the Windows Experience Index is to not get hung-up about it. Although it can be informative, it seems that it is used mostly for Microsoft to obtain data about the hardware on which Windows is run. So just because the score on a machine is on the mid-to-low end, does not mean that the 'lowest' component should be upgraded. Nor should someone look for the computer with the highest Windows Experience Index to purchase.







