当您使用 Windows 10 时,PC 上的内部存储会随着时间逐渐填满。这不是大容量 HDD 和 SSD(capacity HDDs and SSDs)的主要问题。但是你会在启动时遇到与空间相关(breathing room)的障碍(t offer)。
您可以依靠多种方法来释放Windows 10中的磁盘空间。其中一些可以帮助您释放数十(如果不是数百)千兆字节,而另一些则只为您节省几兆字节。

1. 释放回收站
当您删除计算机上的文件时,Windows 10 不会彻底删除它们。相反,它将它们藏在回收站(Recycle Bin)中。如果您以后改变主意(restore deleted files if you change your mind),这允许您恢复已删除的文件。但是您最终为了方便而交易了磁盘空间。(disk space)
如果您不打算(t plan)恢复任何已删除的文件,您可以选择清空回收站(Recycle Bin)。为此,请右键单击桌面上的回收站图标并选择(Recycle Bin)清空回收站(Empty Recycle Bin)。或者,您可以打开回收站(Recycle Bin)并删除其中的选定文件。

也可以在选择文件后按Shift + Delete永久删除文件而不将其发送到(Delete)回收站(Recycle Bin)。
2.清除下载文件夹
Windows 10 PC 上的“下载”文件夹(Downloads folder)是您很少重复使用的垃圾文件和程序安装程序的热点。
打开文件资源管理器,然后在边栏上选择这台电脑(This PC)>下载(Downloads )。然后,删除您不想要的所有文件。您还可以将文件夹切换到列表视图并按(List )大小(Size )过滤文件,以查找和删除占用空间最多的项目。
3.删除不需要的应用程序
从计算机中删除不需要的应用程序和程序(apps and programs)是减少 Windows 10 计算机上已用存储量的另一种快速方法。
为此,请打开“开始(Start )”菜单并转到“设置”(Settings ) > “应用(Apps )程序” > “应用程序和功能”(Apps & Features)。然后,滚动列表,选择不再使用的应用程序,然后选择“(t use)卸载(Uninstall)”将其删除。

4. 在 OneDrive 中按需使用文件
OneDrive 内置于Windows 10中,可让您轻松将文档和照片备份到云端。(back up documents and photos)它还支持文件点播功能(On-Demand functionality),允许您仅在需要时将备份文件下载到本地存储。
要在OneDrive中启用 Files On-Demand,请选择任务栏上的OneDrive图标,然后选择帮助和设置(Help & Settings )>设置(Settings)。在随后显示的Microsoft OneDrive 对话框中,切换到“(Microsoft OneDrive dialog)设置”(Settings )选项卡。通过选中旁边的框节省空间并在使用文件时下载文件(Save space and download files as you use them)。
激活Files On-Demand(Files On-Demand)后,您可以随时通过右键单击并选择(right-clicking and selecting) 释放空间(Free up space)来直接卸载备份的文件和文件夹。您将继续看到项目的占位符图标。尝试访问已卸载的文件应提示OneDrive将其下载到本地。

5.在设置中使用存储窗格
Windows 10 的“设置”应用(Settings app)附带一个“存储”窗格(Storage pane),可帮助您识别占用 PC 上最多存储空间的数据类型。
您可以通过开始(Start )>设置(Settings )>系统(System )>存储(Storage)来访问它。然后,您将看到一个类别列表,例如应用程序和功能(Apps & Features)、临时文件(Temporary Files)、图片(Pictures)、音乐(Music)等,您可以深入了解所有这些类别并删除占用空间的程序和文件。
但是,其中最重要的是Temporary Files。选择它,您会立即看到保存临时文件的区域列表,例如下载文件夹(Downloads folder)、回收站(Recycle Bin)和Windows 更新缓存(Windows Update cache)。接下来(Next),选择您要删除的内容并选择删除文件(Remove files)。

6.运行或激活存储感知
上面的Storage 窗格(Storage pane)还带有一个名为Storage Sense的功能。激活它,您将提供 Windows 10 权限以自动删除计算机上的临时文件。
转到开始(Start )>设置(Settings )>系统(System )>存储(Storage )>配置 Storage Sense 或立即运行它(Configure Storage Sense or run it now)以访问您的Storage Sense设置。
然后,打开Storage Sense下的开关以激活该功能。通过调整设置来确定您希望 Storage Sense 如何在您的计算机上运行。例如,您可以指定它应该何时运行(例如,在磁盘空间(disk space)不足的情况下)、它应该多久删除一次回收站和下载文件夹(Recycle Bin and Downloads folder)中的内容等等。

您还可以选择随时手动运行Storage Sense 。只需滚动(Just scroll)到屏幕底部并选择(screen and select) 立即清洁(Clean now)。
7.使用磁盘清理
如果您喜欢比“设置”应用(Settings app)中的“存储”屏幕(Storage screen)更紧凑的视图,则可以选择旧版磁盘清理实用程序(legacy Disk Cleanup utility)。它提供了类似的功能,并允许您快速删除大量临时文件。您可以通过在“开始”菜单上搜索“磁盘清理”来启动它。(Disk Cleanup)
然后(Follow)选中要删除的数据类型旁边的框,例如Windows 更新清理(Windows Update Cleanup)、Internet 临时文件(Temporary Internet Files)、系统错误内存转储文件(System error memory dump files)等。然后,选择确定(OK)。
您还可以选择清理系统文件(Clean up system files)选项来查看其他临时文件类型。

8.删除更多临时文件
Windows 10 还包含大量其他可以安全删除的临时文件。如需完整的分步演练(step-by-step walkthrough),我们建议您查看有关在 Windows 10 中删除临时文件的(removing temporary files in Windows 10)指南。但这里是简短的过程。
首先按Windows + R打开“运行”框。然后,键入%temp%并选择OK。
然后(Follow)删除显示的目录中的所有文件和文件夹。接下来,在另一个运行框中键入temp ,选择(temp )OK,然后删除该目录中的所有文件。最后,通过重新启动计算机来结束。

9.清除浏览器缓存
当您上网时,您的浏览器最终会缓存数据以加快后续网站访问速度。但是,如果您急需存储空间,您可以通过清除浏览器缓存(browser cache)快速释放大约 500 MB 到 1 GB 的存储空间。
谷歌浏览器(Google Chrome)
打开Chrome菜单并选择设置(Settings)>隐私和安全(Privacy and security )>清除浏览数据(Clear browsing data)。
在随后显示的清除浏览数据对话框中,将时间范围(Time range )设置为所有时间并选中(All time)缓存图像和文件(Cached images and files)旁边的框。最后,选择清除数据(Clear data)。

火狐浏览器(Mozilla Firefox)
打开Firefox菜单并转到选项(Options)>隐私和安全(Privacy and security)>清除数据(Clear Data)(在Cookie 和站点数据(Cookies and Site Data)部分下)。然后,选中Cached Web Content(Cached Web Content)旁边的框并选择Clear。
微软边缘(Microsoft Edge)
打开边缘(Edge )菜单并选择设置(Settings)。然后,切换到侧边栏上的隐私、搜索和服务(Privacy, search, and services )选项卡,然后在清除浏览数据(Clear browsing data)下选择选择要清除(Choose what to clear )的内容。
接下来,将Time range设置为All time ,选中(All time)Cached images and files旁边的框,然后选择Clear data。
WinDirStat是一个免费的开源应用程序,可让您以可视格式查找计算机上的大型文件和文件夹。安装并打开程序后,选择要扫描的存储驱动器或分区。(storage drive or partition)然后,您应该会看到占用最多存储空间的目录列表,包括相对于驱动器大小的百分比形式。(percentage form relative)

一旦WinDirStat完成扫描驱动器,您还应该看到许多彩色块表示所选驱动器(chosen drive)上的文件(按格式) 。尺寸越大,它们占用的空间就越多。您可以右键单击一个项目并选择(item and select) Explorer Here以在(Explorer Here)File Explorer中查看(和删除)它。
11.删除休眠文件
Windows 10 的休眠模式(Hibernate mode)允许您在关闭计算机后恢复文件和程序。但是通过保存程序和操作系统的状态来促进功能的文件可能会占用大量磁盘空间(disk space)。因此,如果您不介意(t mind)跳过使用Hibernate,您可以选择禁用它并回收存储空间。
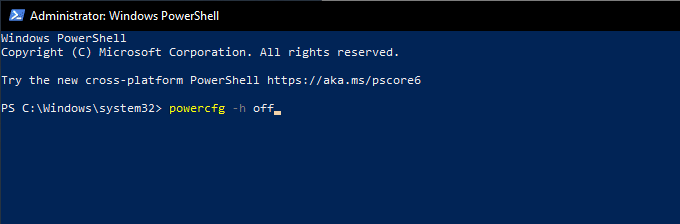
为此,请右键单击开始(Start )按钮并选择Windows PowerShell (Admin)。然后,运行以下命令:
powercfg -h 关闭(powercfg -h off)
通过打开文件资源管理器(File Explorer)来跟随它。然后,选择File > Change folder and search options。
在随后显示的“文件夹选项”对话框中,切换到“(Folder Options dialog)查看”(View )选项卡并选择“显示隐藏的文件、文件夹和驱动器”(Show hidden files, folder, and drives)。最后,打开Windows 10 安装驱动器 —(installation drive—)本地磁盘 (C:)(Local Disk (C:)) — 并删除标记为hiberfil.sys的文件。
有关完整的分步说明,请查看本指南以禁用 Windows 10 中的休眠(disabling Hibernation in Windows 10)。
12.删除旧用户帐户
如果您的计算机有多个 Windows 10 用户帐户(multiple Windows 10 user accounts),您可能需要删除任何不再有用的帐户。请注意(Just note),您将永久丢失与您删除的帐户相关的所有数据。
首先打开计算机上的“开始(Start )”菜单。然后,转到设置(Settings )>帐户(Accounts )>家庭和其他用户(Family & other users),从其他用户(Other users )部分选择一个帐户,然后选择删除(Remove)。

13.禁用系统还原
系统还原(System Restore)是一种方便的备份功能(backup function),可帮助您在出现问题时将计算机还原到较早的状态。但它也使用了大量的存储空间。因此,如果您的存储空间仍然不足,您可以选择删除除最后一个系统还原点(System Restore point)之外的所有内容。
为此,请打开磁盘清理(Disk Cleanup)实用程序,选择清理系统文件(Clean up system files),切换到更多选项选项(More Options)卡,然后选择清理(Clean up)>删除(Delete)。

如果您不介意完全禁用系统还原(disabling System Restore),请打开“运行”框(Run box),键入sysdm.cpl,然后选择“确定(OK)” 。在显示的系统(System) 属性(Properties)对话框中,选择保护设置(Protection Settings )下的配置(Configure ),然后选择禁用系统保护(Disable system protection)旁边的单选按钮(radio button)。

14. 减小 Windows 10 的大小
您可以通过激活一项名为CompactOS的功能来减小(CompactOS)Windows 10本身的大小以释放磁盘空间。它略微压缩了操作系统(operating system),非常值得在剩余存储空间很少的计算机上激活。
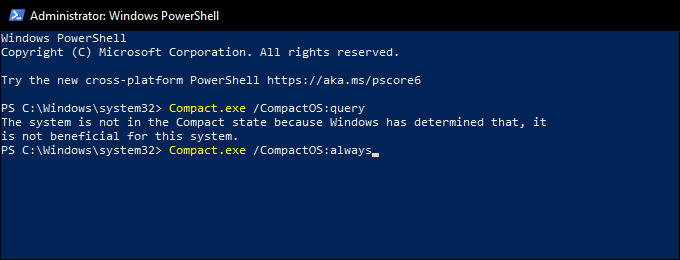
首先右键单击“开始(Start )”按钮。然后,选择Windows PowerShell (Admin)并运行以下命令:
Compact.exe /CompactOS:query
如果您发现CompactOS在您的系统上尚未激活,请运行以下命令来激活它:
Compact.exe /CompactOS:always
15.禁用保留存储
Windows 10 使用一项称为保留存储(Reserved Storage)的功能来确保它有足够的空间来下载和安装未来的操作系统更新。但这也意味着丢失了数 GB 的存储空间。因此,您可以根据需要选择通过调整系统注册表来(system registry)禁用保留存储(disable Reserved Storage)。
首先按Windows + R打开“运行”框。然后,键入regedit并选择OK。在随后显示的注册表编辑器窗口(Registry Editor window)中,在地址栏中键入以下路径并按(address bar and press) Enter:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager

然后双击ShippedWithReserves键。然后,选择Value Data to 0,选择OK,然后退出注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。您必须重新启动计算机才能使更改生效。
释放大量空间
上面的提示绝对可以帮助您释放Windows 10中的磁盘空间。花时间单独设置Storage Sense是阻止自己定期进行手动清洁的好方法。但是,当您需要更多存储空间时,再次浏览列表可以帮助您回收 PC 上大量已用完的空间。
15 Ways to Free Up Disk Space in Windows 10
When you use Windows 10, the internal storage on your PC fills up gradually over tіme. That’ѕ not a major problem on high capacity HDDs and SSDs. But you’ll run into spaсe-related snags on drives that don’t offer much breathing room to start with.
You can rely on several methods to free up disk space in Windows 10. Some of them help you free up tens (if not hundreds) of gigabytes, while others net you only a few extra megabytes.

1. Free Up Recycle Bin
When you delete files on your computer, Windows 10 does not remove them outright. Instead, it stashes them away in the Recycle Bin. That allows you to restore deleted files if you change your mind later. But you end up trading disk space for convenience.
If you don’t plan on restoring any deleted files, you can choose to empty the Recycle Bin. To do that, right-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop and select Empty Recycle Bin. Alternatively, you can open the Recycle Bin and remove select files inside it.

It’s also possible to delete a file permanently without sending it to the Recycle Bin by pressing Shift + Delete after selecting it.
2. Clear the Downloads Folder
The Downloads folder on your Windows 10 PC is a hotspot for junk files and program installers that you’ll rarely ever re-use.
Open File Explorer and select This PC > Downloads on the sidebar. Then, delete any files that you don’t want. You can also switch the folder to List view and filter files by Size to locate and remove items that use up space the most.

3. Delete Unwanted Apps
Getting rid of unwanted apps and programs from your computer is another quick way to cut down the amount of used storage on your Windows 10 computer.
To do that, open the Start menu and go to Settings > Apps > Apps & Features. Then, scroll through the list, pick the apps you don’t use anymore, and select Uninstall to delete them.

4. Use Files On-Demand in OneDrive
OneDrive comes built into Windows 10 and allows you to back up documents and photos to the cloud easily. It also supports Files On-Demand functionality, allowing you to download backed-up files to local storage only when needed.
To enable Files On-Demand in OneDrive, select the OneDrive icon on the taskbar and choose Help & Settings > Settings. On the Microsoft OneDrive dialog box that then shows up, switch to the Settings tab. Follow that by checking the box next to Save space and download files as you use them.
With Files On-Demand active, you can directly offload backed-up files and folders whenever you want by right-clicking and selecting Free up space. You’ll continue to see placeholder icons of the items. Attempting to access an offloaded file shall prompt OneDrive to download it locally.

5. Use Storage Pane in Settings
Windows 10’s Settings app comes with a Storage pane to help you identify data types that use up the most amount of storage on your PC.
You can access it by going to Start > Settings > System > Storage. You’ll then see a list of categories such as Apps & Features, Temporary Files, Pictures, Music, etc., all of which you can dive into and remove space-consuming programs and files.
However, the most important of the lot is Temporary Files. Select it, and you’ll immediately come across a list of areas that hold temporary files, such as the Downloads folder, Recycle Bin, and Windows Update cache. Next, pick what you want to delete and select Remove files.

6. Run or Activate Storage Sense
The Storage pane above also comes with a feature called Storage Sense. Activate it, and you provide Windows 10 permissions to delete temporary files on your computer automatically.
Go to Start > Settings > System > Storage > Configure Storage Sense or run it now to access your Storage Sense settings.
Then, turn on the switch under Storage Sense to activate the feature. Follow that by tweaking the settings to determine how you want Storage Sense to run on your computer. For example, you can specify when it should run (while low on disk space, for example), how often it should delete the contents inside your Recycle Bin and Downloads folder, and so on.

You can also choose to run Storage Sense manually whenever you want. Just scroll to the bottom of the screen and select Clean now.
7. Use Disk Cleanup
If you prefer a more compact view than the Storage screen in the Settings app, you can opt for the legacy Disk Cleanup utility instead. It offers similar functionality and allows you to delete loads of temporary files quickly. You can bring it up by searching for Disk Cleanup on the Start menu.
Follow by checking the boxes next to the data types you want to delete—e.g., Windows Update Cleanup, Temporary Internet Files, System error memory dump files, etc. Then, select OK.
You can also select the Clean up system files option to view additional temporary file types.

8. Delete More Temporary Files
Windows 10 also contains large amounts of other temporary files that you can safely delete. For a complete step-by-step walkthrough, we recommend checking out this guide about removing temporary files in Windows 10. But here’s the process in brief.
Start by pressing Windows + R to open the Run box. Then, type %temp% and select OK.
Follow by deleting all files and folders within the directory that shows up. Next, type temp into another Run box, select OK, and remove all files inside that directory as well. Finally, wrap up by restarting your computer.

9. Clear Browser Cache
When you surf the internet, your browser ends up caching data to make subsequent website visits faster. But if you’re crunched for storage, you can quickly free up roughly 500 megabytes to one gigabyte of storage by clearing the browser cache.
Google Chrome
Open the Chrome menu and select Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data.
On the Clear browsing data dialog that then shows up, set Time range to All time and check the box next to Cached images and files. Finally, select Clear data.

Mozilla Firefox
Open the Firefox menu and go to Options > Privacy and security > Clear Data (under the Cookies and Site Data section). Then, check the box next to Cached Web Content and select Clear.
Microsoft Edge
Open the Edge menu and select Settings. Then, switch to the Privacy, search, and services tab on the sidebar and select Choose what to clear under Clear browsing data.
Next, set the Time range to All time, check the box next to Cached images and files, and select Clear data.
10. Find Large Files With WinDirStat
WinDirStat is a free and open-source app that allows you to locate large files and folders on your computer in visual format. After installing and opening the program, pick the storage drive or partition you want to scan. You should then see a list of directories that occupy the most storage, including in percentage form relative to drive size.

Once WinDirStat finishes scanning the drive, you should also see many colored blocks denoting files (by format) on the chosen drive. The larger the size, the more space they consume. You can right-click an item and select Explorer Here to view (and delete) it in File Explorer.
11. Delete Hibernation File
Windows 10’s Hibernate mode allows you to restore files and programs even after you’ve powered down your computer. But the file that facilitates the functionality by saving the state of the programs and operating system can hog up a lot of disk space. So if you don’t mind skipping out on using Hibernate, you can choose to disable it and reclaim the storage.
To do that, right-click the Start button and select Windows PowerShell (Admin). Then, run the command below:
powercfg -h off

Follow that by opening File Explorer. Then, select File > Change folder and search options.
On the Folder Options dialog box that then shows up, switch to the View tab and select Show hidden files, folder, and drives. Finally, open the Windows 10 installation drive—Local Disk (C:)—and delete the file labeled hiberfil.sys.
For complete step-by-step instructions, check out this guide to disabling Hibernation in Windows 10.
12. Delete Old User Accounts
If your computer has multiple Windows 10 user accounts, you might want to delete any that don’t serve a purpose anymore. Just note that you’ll permanently lose all data related to the accounts you remove.
Start by opening the Start menu on your computer. Then, go to Settings > Accounts > Family & other users, select an account from the Other users section, and select Remove.

13. Disable System Restore
System Restore is a handy backup function that helps you restore your computer to an earlier state should something go wrong. But it also uses a hefty chunk of storage. So if you’re still running low on storage, you can choose to delete all but the last System Restore point.
To do that, open the Disk Cleanup utility, select Clean up system files, switch to the More Options tab, and select Clean up > Delete.

If you don’t mind disabling System Restore completely, open the Run box, type sysdm.cpl, and select OK. On the System Properties dialog box that shows up, select Configure under Protection Settings and select the radio button next to Disable system protection.

14. Reduce the Size of Windows 10
You can tone down the size of Windows 10 itself to free up disk space by activating a feature called CompactOS. It compresses the operating system slightly and is well worth activating on computers with very little storage space remaining.
Start by right-clicking the Start button. Then, select Windows PowerShell (Admin) and run the following command:
Compact.exe /CompactOS:query
If you see that CompactOS isn’t already active on your system, run the following command to activate it:
Compact.exe /CompactOS:always

15. Disable Reserved Storage
Windows 10 uses a feature called Reserved Storage to ensure it has sufficient space to download and install future operating system updates. But that also translates to multiple gigabytes of lost storage. So, you can choose to disable Reserved Storage with a tweak to the system registry should you want.
Start by pressing Windows + R to open the Run box. Then, type regedit and select OK. On the Registry Editor window that shows up subsequently, type the following path into the address bar and press Enter:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager

Follow that by double-clicking the ShippedWithReserves key. Then, select Value Data to 0, select OK, and exit the Registry Editor. You must restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Lots of Space Freed Up
The pointers above should’ve definitely helped you free up disk space in Windows 10. Taking the time to set up Storage Sense alone is a great way to stop yourself from going on manual cleaning sessions regularly. But whenever you want more storage, working your way through the list again can help you reclaim large amounts of used-up space on your PC.

















