在Windows 10中,知道如何以管理员身份运行程序非常重要。默认情况下,Windows 10中的(Windows 10)应用和游戏(apps and games)在没有管理员权限的情况下运行,以防止对您的系统进行未经授权的更改。但是,有时某些程序需要管理员权限才能正常工作或运行特定命令。Windows 10使您能够以管理员身份运行程序,而无需禁用任何东西。以下是在 Windows 10 中的任何桌面应用程序上使用“以管理员身份运行”的所有方法:("Run as administrator")
第一(First)件事:关于UAC 和(UAC and Run)以管理员身份运行
在早期版本的Windows中,应用程序具有系统范围的权限,这是一个安全风险(security risk)。从Windows Vista(Windows Vista)开始,包括Windows 10在内的所有Microsoft操作系统都包括UAC或用户帐户控制(User Account Control),这是一种防止未经授权更改操作系统的(operating system)安全功能(security feature)。尝试以管理员身份运行应用程序是需要管理权限的更改之一。在启动所选程序之前,会触发UAC提示,请求许可。如果您从没有管理员权限的帐户运行应用程序,则UAC提示要求您输入管理员密码(administrator password)。没有管理员密码(admin password),程序不会启动。

在Windows 10中,如果它是桌面应用程序,您只能运行具有管理员权限的程序。其中一些应用程序,如安全软件(security software),在没有管理权限的情况下无法正常运行。从Microsoft Store安装的(Microsoft Store)Windows应用程序无法在Windows 10中以管理权限运行。此外,他们拥有与普通用户帐户(user account)相同级别的权限,因此不允许他们更改高级系统设置或Windows 注册表(Windows Registry)。
您可以通过阅读什么是Windows 应用程序(Windows app)来了解有关桌面应用程序和 UWP 应用程序(desktop apps and UWP apps)之间区别的更多信息,并确定哪些可以“以管理员身份运行("Run as administrator")” 它与桌面应用程序(desktop app)或程序有何不同?
1.从开始菜单(Start Menu)快捷方式或磁贴的上下文菜单中以管理员身份运行程序
在Windows 10中,您可以使用其(Windows 10)开始菜单(Start Menu)快捷方式的上下文菜单启动具有管理权限的程序。首先,打开开始菜单(Start Menu)。然后,在“所有应用程序(All apps)”列表中找到要启动的程序的快捷方式,然后右键单击或按住它以打开上下文菜单。单击(Click)、点击或将鼠标悬停在更多(More)选项上,然后单击或点击“以管理员身份运行("Run as administrator)”。

如果您的桌面应用程序(desktop app)在“开始”菜单(Start Menu)中有可用的磁贴,请右键单击或按住它以打开上下文菜单。访问更多(More),然后单击或点击“以管理员身份运行("Run as administrator)”。
2.在其开始菜单(Start Menu)快捷方式或磁贴上使用“ Ctrl + Shift + Click”以管理员身份运行(Run)
打开“开始”菜单(Start Menu)并找到要以管理员身份启动的程序的快捷方式。按住键盘上的Ctrl和Shift键,然后单击或点击该程序的快捷方式。

您还可以在应用程序的“开始”菜单磁贴上使用(Start Menu)"Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap"快捷方式在Windows 10中以管理员权限运行它。
在我们的测试期间,这种方法并非每次都有效,因此如果您遇到这种情况,请重试或考虑以其他方式以管理员身份运行应用程序。
3.从桌面快捷方式以管理员身份运行程序(desktop shortcut)
找到您想以管理员身份运行的程序的桌面快捷方式或自己创建一个。(desktop shortcut)然后,右键单击或按住它以打开上下文菜单。单击(Click)或点击“以管理员身份运行”("Run as administrator")选项。

4.从任务栏快捷方式(taskbar shortcut)以管理员身份运行桌面应用程序(desktop app)
在Windows 10中,您还可以从其任务栏快捷方式运行具有管理员权限的(taskbar shortcut)桌面应用程序(desktop app)。右键单击或按住快捷方式,然后再次右键单击或按住(right-click or press-and-hold)程序名称。然后,从打开的菜单中,选择“以管理员身份运行”("Run as administrator)。

您还可以使用应用程序任务栏快捷方式上的(taskbar shortcut)"Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap"Windows 10中以管理员权限运行它。
5.从右键菜单以管理员身份运行程序
虽然更容易找到,但快捷方式并不是在Windows 10中以管理员身份运行程序的唯一方法。您可以从主可执行文件的上下文菜单中执行相同的操作。
打开文件资源管理器(Open File Explorer)并找到桌面应用程序(desktop app)的可执行文件。右键单击或按住它以打开上下文菜单,然后单击或点击“以管理员身份运行("Run as administrator)”。

6.使用文件资源管理器(File Explorer)功能区中的“以管理员身份运行”(Run)
在文件资源管理器(File Explorer)中找到程序的主要可执行文件。选择它,然后单击或点击功能区中的“管理(Manage)”选项卡。

您需要的选项显示在Application Tools的(Application Tools)Run部分。单击或点击(Click)“以管理员身份运行”("Run as administrator")按钮的上半部分以授予所选应用管理员(app admin)权限。
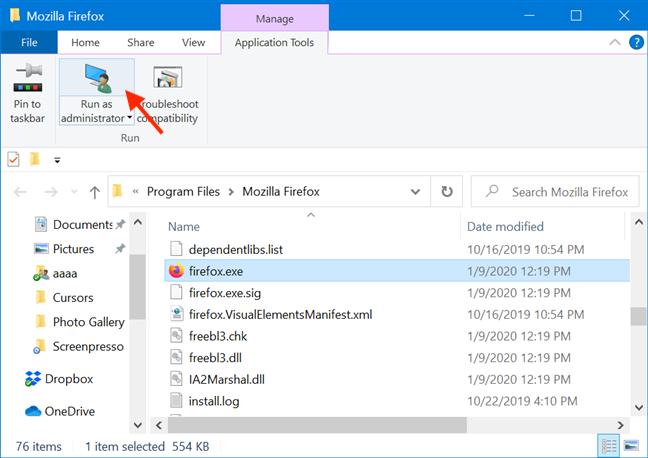
作为替代方案,您也可以按“以管理员身份运行”("Run as administrator")按钮的下半部分,然后单击或点击下拉菜单中的“以管理员身份运行”选项。("Run as administrator")

7. 从“搜索”窗口(Search window)以管理员身份运行桌面应用程序(desktop app)
在任务栏搜索字段中(taskbar search field),输入需要以管理员权限运行的程序的名称。然后,单击或点击(click or tap)搜索(Search)窗口右侧显示的“以管理员身份运行”选项。("Run as administrator")

显然,当您看到UAC 提示(UAC prompt)要求以管理员身份运行应用程序时,单击或点击(click or tap) Yes。
8. 在任务栏搜索结果中使用“ (taskbar search result)Ctrl + Shift + Enter ”以管理员身份运行程序
在任务栏的搜索字段(search field)中输入程序的名称。如果有多个结果,请使用键盘上的箭头键突出显示您要以管理员身份运行的程序。然后,同时按键盘上的Ctrl + Shift + Enter键。

9. 从“运行”窗口(Run window)以管理员身份运行程序
打开“运行”窗口并输入(Run window and type)要以管理员身份运行的程序的可执行文件的名称。然后按住键盘上的Ctrl和Shift键,然后单击(keyboard and click)或点击OK。

或者,在输入程序的主要可执行文件的名称后,同时按键盘上的Ctrl + Shift + Enter键。

10.从任务管理器以管理员身份(Task Manager)运行(Run)
在Windows 10(Windows 10)中以管理员身份启动程序的另一种方法是使用任务管理器(Task Manager)启动它。首先,打开任务管理器(Task Manager)。然后,如果它在其紧凑视图中打开,请单击或点击(click or tap)更多详细信息(More details)按钮。

在展开的任务管理器(Task Manager)中,打开文件(File)菜单并单击或点击“运行新任务("Run new task)”。

这将打开“创建新任务”("Create new task")窗口。您可以使用其打开(Open)字段输入要以管理员身份启动的程序的路径,或者您可以单击或点击浏览(Browse)以导航到它。然后,确保选中“使用管理权限创建此任务”。("Create this task with administrative privileges.")选项,然后单击或点击OK。

提示:(TIP:)使用此方法以管理员身份启动程序的一个优点是您可以跳过该过程的UAC部分。这是因为该应用程序自动继承了任务管理器(Task Manager)的权限——在我们的例子中是管理员权限——所以你所要做的就是选中复选框以启用该选项,如上所示。如果您在设备上只有标准用户权限,则该选项会丢失。

11. 使用命令提示符(Command Prompt)( CMD ) 或PowerShell中的(PowerShell)RunAs 命令(RunAs command)以管理员身份运行桌面应用程序(desktop app)
如果命令行(command line)是您最喜欢让计算机执行所需操作的方式,您还可以访问命令提示符或 PowerShell(access Command Prompt or PowerShell)以管理员身份运行程序。在CMD 或 PowerShell 窗口(CMD or PowerShell window)中输入以下命令,根据需要进行调整:
runas /user:" your_computer_name\administrator_name" " C:\path\program.exe "
将your_computer_name替换为您的计算机名称,将administrator_name替换为系统管理员(administrator_name)用户帐户(user account)的名称,并将C:\path\program.exe替换为您要以管理员身份运行的程序的完整路径。
如下图所示,如果您输入正确的命令,您还需要输入管理员密码。然后,再次按键盘上的Enter 。

提示:(TIP:)使用此方法以管理员身份启动程序,您可以跳过该过程的UAC部分。
12. 始终以管理员权限运行程序
为避免在定期访问的桌面应用程序(desktop apps)上不断使用上述方法,您可以将程序设置为始终以管理员权限运行。
首先,打开文件资源管理器(File Explorer)并找到要运行的程序的主要可执行文件。右键单击或(Right-click or press)按住它以打开上下文菜单。然后,单击或点击(click or tap)属性(Properties)。

在“属性(Properties)”窗口中,转到“兼容性(Compatibility)”选项卡。在窗口底部,选中“以管理员身份运行此程序”("Run this program as an administrator")选项旁边的框,然后单击或点击应用(Apply)或确定(OK)。

应用此设置,并且从现在开始,程序始终以管理员权限运行。如果要禁用该选项,请按照相同的步骤操作。您还可以编辑程序快捷方式的属性(Properties)以避免篡改其主要可执行文件。首先,右键单击或按住程序的快捷方式以访问其上下文菜单,然后单击或点击(click or tap)Properties。

然后,在快捷方式的“属性(Properties)”窗口中,选择“快捷方式(Shortcut)”选项卡。单击或点击高级(Advanced)按钮以打开高级属性(Advanced Properties)。
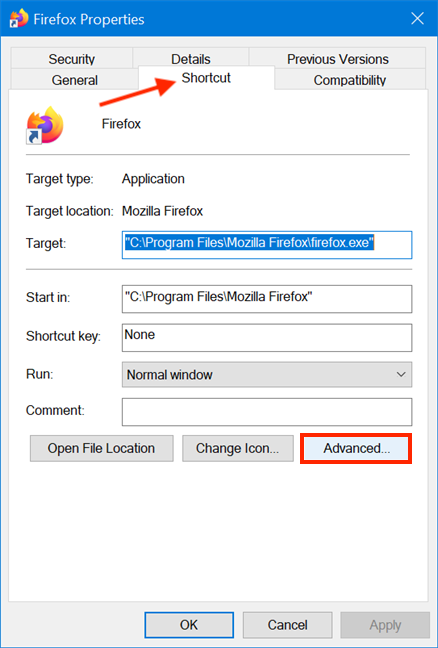
在“高级属性”窗口中,选中(Advanced Properties)“以管理员身份运行”("Run as administrator")旁边的框,然后单击或点击“确定(OK)” 。

最后,您将返回到“属性(Properties)”窗口,您必须在其中单击或点击OK或Apply,您就完成了。

应用设置,只要您使用相同的快捷方式打开程序,您的程序就可以使用管理权限。当您使用本节中的方法时,UAC会在您尝试启动应用程序时立即提示您。
13. 运行具有管理员权限且没有UAC 提示的程序(UAC prompt)
使用任务计划程序(Task Scheduler),您可以以管理员身份运行程序,而无需每次都收到UAC(用户帐户控制)的提示。(UAC (User Account Control))这很简单,您不必禁用UAC,从而损害Windows 10的安全性。我们整理了一份详细的分步指南(step guide)来帮助您:使用Windows 任务计划(Windows Task Scheduler)程序在没有UAC提示和管理员权限的情况下运行应用程序。
您打算使用哪种方法?
在Windows 10中,与旧版本的(Windows 10)Windows相比,需要以管理员权限运行的应用程序更少。但是,一些合法程序仍然需要提升的权限。要记住的主要事情是,即使您使用管理员帐户(administrator account)登录,您也经常以标准用户身份运行应用程序。这意味着,如果您需要运行需要管理员权限的程序,您只需使用上述方法之一,然后在UAC提示符中批准即可。您打算使用说明的哪种方法?(Which)你(Did)已经使用了其中的一些吗?在评论中告诉我们。
13 ways to use "Run as administrator" in Windows 10 -
In Windows 10, knowing how to run programs as administrator is very important. By default, apps and games in Windows 10 run without administrator permissiоns, to prevent unauthorized changеs to your system. Howеver, there are times when sоme programs require administrator permissions to work properly or to run specіfic commands. Windows 10 offers you the abіlity to rυn programs as аdmin without having to diѕable аnything. Hеre are all the methods to use "Run as administrator" on any desktop app in Windows 10:
First things first: About UAC and Run as administrator
In early versions of Windows, applications had system-wide privileges, which was a security risk. All of Microsoft's operating systems from Windows Vista onward, including Windows 10, include UAC or User Account Control, a security feature that prevents unauthorized changes to the operating system. Trying to run an application as administrator is one of the changes that require administrative privileges. Before the selected program is launched, a UAC prompt is triggered, asking for permission. If you run the application from an account without administrator permissions, the UAC prompt asks you to enter an administrator password. Without the admin password, the program does not launch.

In Windows 10, you can only run a program with administrator permissions if it is a desktop app. Some of these applications, like security software, cannot run correctly without having administrative permissions. Windows apps that are installed from the Microsoft Store cannot be run with administrative privileges in Windows 10. Furthermore, they have the same level of permissions as a normal user account, so they are not allowed to make changes to advanced system settings or the Windows Registry.
You can learn more about the difference between desktop apps and UWP apps and figure out which ones you can "Run as administrator" by reading What is a Windows app? How is it different from a desktop app or a program?.
1. Run a program as admin from the contextual menu of its Start Menu shortcut or tile
In Windows 10, you can launch a program with administrative permissions by using the contextual menu of its Start Menu shortcut. First, open the Start Menu. Then, find the shortcut of the program you want to launch in the All apps list, and right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Click, tap, or hover over the More option, and then click or tap on "Run as administrator."

If you have a tile for your desktop app available in the Start Menu, right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Access More and then click or tap on "Run as administrator."
2. Run as administrator using "Ctrl + Shift + Click" on its Start Menu shortcut or tile
Open the Start Menu and locate the shortcut of the program you want to launch as administrator. Hold down both the Ctrl and the Shift keys on your keyboard and then click or tap on that program's shortcut.

You can also use the "Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap" shortcut on an app's Start Menu tile to run it with administrator permissions in Windows 10.
During our tests, this method did not work every time, so if that is the case for you, either try again or consider running the app as administrator another way.
3. Run a program as administrator from its desktop shortcut
Find the desktop shortcut for the program you want to run as admin or create one yourself. Then, right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Click or tap on the "Run as administrator" option.

4. Run a desktop app as administrator from its taskbar shortcut
In Windows 10, you can also run a desktop app with administrator permissions from its taskbar shortcut. Right-click or press-and-hold on the shortcut, and then right-click or press-and-hold again on the program's name. Then, from the menu that opens, choose "Run as administrator."

You can also use the "Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap" shortcut on an app's taskbar shortcut to run it with administrator permissions in Windows 10.
5. Run a program as administrator from its right-click menu
Although easier to find, shortcuts are not the only way to run a program as administrator in Windows 10. You can perform the same action from the main executable file's contextual menu.
Open File Explorer and find the desktop app's executable. Right-click or press-and-hold on it to open the contextual menu, and then click or tap on "Run as administrator."

6. Use "Run as administrator" from File Explorer's ribbon
Find the program's main executable in File Explorer. Select it, and then click or tap on the Manage tab from the ribbon.

The option you need is displayed in the Run section of Application Tools. Click or tap on the upper half of the "Run as administrator" button to give the selected app admin permissions.

As an alternative, you can also press the lower half of the "Run as administrator" button and then click or tap on the "Run as administrator" option from the drop-down menu.

7. Run a desktop app as admin from the Search window
In the taskbar search field, type in the name of the program that needs to run with administrator permissions. Then, click or tap on the "Run as administrator" option displayed on the right side of the Search window.

Obviously, when you see the UAC prompt asking for permission to run the app as admin, click or tap Yes.
8. Run a program as administrator using "Ctrl + Shift + Enter" on its taskbar search result
Type the name of the program in your taskbar's search field. If there are multiple results, use the arrow keys on your keyboard to highlight the program you want to run as administrator. Then, simultaneously press the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys on your keyboard.

9. Run a program as administrator from the Run window
Open the Run window and type in the name of the executable for the program you want to run as administrator. Then hold down the Ctrl and Shift keys on your keyboard and click or tap on OK.

Alternatively, after typing in the name of the program's main executable, press the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys on your keyboard at the same time.

10. Run as admin from the Task Manager
Another way to launch a program as administrator in Windows 10 is to start it using the Task Manager. To begin, open the Task Manager. Then, if it opens up in its compact view, click or tap on the More details button.

In the expanded Task Manager, open the File menu and click or tap on "Run new task."

This opens the "Create new task" window. You can use its Open field to enter the path to the program you want to launch as administrator, or you can click or tap on Browse to navigate to it. Then, make sure to check the "Create this task with administrative privileges." option and click or tap on OK.

TIP: An advantage of using this method to launch programs as administrator is that you skip the UAC part of the process. That is because the app automatically inherits the permissions of the Task Manager - in our case, administrator permissions - so all you have to do is check the box to enable the option, as seen above. The option is missing if you only have standard user permissions on the device.

11. Run a desktop app as admin using the RunAs command in Command Prompt (CMD) or PowerShell
If the command line is your favorite way of asking your computer to do what you want, you can also access Command Prompt or PowerShell to run a program as administrator. Enter the following command in the CMD or PowerShell window, adjusting it to fit your needs:
runas /user:"your_computer_name\administrator_name" "C:\path\program.exe"
Replace your_computer_name with your computer's name, administrator_name with the name of a user account that is an administrator on your system, and C:\path\program.exe with the complete path to the program that you want to run as administrator.
As seen in the image below, if you enter the command correctly, you are also asked to enter the administrator's password. Then, press Enter on your keyboard once again.

TIP: Using this method to launch programs as administrators, you skip the UAC part of the process.
12. Always run a program with administrator permissions
To avoid constantly having to use the methods illustrated above on desktop apps accessed on a regular basis, you can set a program to always run with administrator permissions.
First, open File Explorer and find the main executable of the program you want to run. Right-click or press and hold on it to open the contextual menu. Then, click or tap on Properties.

In the Properties window, go to the Compatibility tab. At the bottom of the window, check the box next to the "Run this program as an administrator" option, and then click or tap on Apply or OK.

This setting is applied, and, from now on, the program always runs with administrator permissions. Follow the same steps if you want to disable the option. You can also edit the Properties of a program's shortcut to avoid tampering with its main executable. To begin, right-click or press-and-hold on a program's shortcut to access its contextual menu, and click or tap on Properties.

Then, in the shortcut's Properties window, select the Shortcut tab. Click or tap on the Advanced button to open Advanced Properties.

In the Advanced Properties window, check the box next to "Run as administrator" and then click or tap OK.

Finally, you are returned to the Properties window, where you have to click or tap on OK or Apply, and you are done.

The settings are applied, and your program works with administrative permissions as long as you open it using the same shortcut. When you use the methods in this section, the UAC prompts you as soon as you try to launch the app.
13. Run a program with administrator permissions and without a UAC prompt
Using the Task Scheduler, you can run a program as administrator without being prompted by the UAC (User Account Control) every time. It is simple, and you don't have to disable UAC, thus compromising Windows 10's security. We put together a detailed step by step guide to help you: Use the Windows Task Scheduler to run apps without UAC prompts and admin rights.
Which method(s) do you plan to use?
In Windows 10, there are fewer apps that need to run with administrator permissions than in older versions of Windows. However, a few legitimate programs still require elevated privileges. The main thing to remember is that even if you are logged in with an administrator account, you regularly run apps as a standard user. This means that if you need to run a program that requires administrator permissions, you can just use one of the methods described above and then approve it in the UAC prompt. Which of the method(s) illustrated do you plan to use? Did you already use some of them? Let us know in a comment.
























