Windows 操作系统(Windows operating system)目前在个人电脑领域占有 96% 的市场份额。为了利用这个机会,硬件制造商尝试开发能够为现有计算机构建添加大量功能的产品。
但这些都不是标准化的。每个制造商都使用自己的软件功能,这些功能是封闭源代码,以使其与竞争对手区分开来。
如果每个硬件都不一样,操作系统怎么知道如何使用硬件呢?
这由设备驱动程序负责。由于 Windows 无法构建对地球上所有硬件设备的支持,因此他们将其留给硬件制造商来开发兼容的驱动程序。
Windows 操作系统(Windows Operating System)只为我们提供了一个界面来与系统上已安装的设备和驱动程序进行交互。这个界面称为设备管理器。(Device Manager.)

什么是设备管理器?(What is a Device Manager?)
它是Microsoft Windows操作系统的一个软件组件,它就像一个连接到系统的所有硬件外围设备的指挥中心。它的工作方式是向我们简要介绍计算机中运行的所有 Windows 认可的硬件设备。
这可能是电子组件,例如键盘、鼠标、显示器、硬盘驱动器、处理器等。它是一种管理工具,是Microsoft 管理控制台(Microsoft Management Console)的一部分。
设备管理器(Device Manager)预装了操作系统,但是,市场上还有其他第三方程序可用于实现相同的预期结果,但由于固有的安全风险,建议不要安装这些第三方应用程序他们拥有。
(Microsoft)随着Windows 95的推出, (Windows 95)Microsoft开始将此工具与操作系统捆绑在一起。最初,它只是为了显示现有硬件并与之交互而设计的。在接下来的几个版本中,添加了热插拔功能,这使内核能够通知设备管理器任何新的硬件相关更改正在发生。例如插入U(USB)盘、插入新的网线等。
设备管理器帮助我们:(Device Manager helps us to:)
- 修改硬件配置。
- 更改和检索硬件驱动程序。
- 检测插入系统的硬件设备之间的冲突。
- 识别(Identify)有问题的驱动程序并禁用它们。
- 显示设备制造商、型号、分类设备等硬件信息。
为什么我们需要设备管理器?
我们可能需要设备管理器的原因有很多,但我们需要设备管理器的最重要原因是软件驱动程序。
软件驱动程序是Microsoft定义的允许您的计算机与硬件或设备通信的软件。但是为什么我们需要它,所以假设您有一张声卡,您应该可以在没有驱动程序的情况下将其插入,并且您的音乐播放器应该生成声卡应该产生的数字信号。
如果只存在一张声卡,这基本上就是它的工作方式。但真正的问题是,实际上有数以千计的声音设备,而且它们的工作方式完全不同。
为了使一切正常工作,软件制造商需要用专门的信号为您的声卡以及曾经存在的每张卡以及将要存在的每张卡重写他们的软件。
因此,软件驱动程序在某种程度上充当抽象层或翻译器,其中软件程序只需以一种标准化语言与您的硬件交互,驱动程序处理其余部分。
另请阅读:(Also Read:) 什么是碎片和碎片整理(What is Fragmentation and Defragmentation)
为什么驱动程序会引起这么多问题?
我们的硬件设备具有系统需要以特定方式进行交互的许多功能。尽管存在标准来帮助硬件制造商制作完美的驱动程序。还有其他设备和其他软件可能会导致冲突。此外,还需要为多个操作系统(如Linux、Windows等)维护单独的驱动程序。
每个都有自己的通用语言,驱动程序需要将其翻译成它。这为特定硬件的驱动程序变体之一留下了足够的空间,使其存在一两个缺陷。
如何访问设备管理器?
我们可以通过多种方式访问设备管理器,在大多数Microsoft Windows 版本中,我们可以从命令提示符、控制面板、运行工具、右键单击开始菜单等打开设备管理器。
方法一:从开始菜单(Method 1: From the start menu)
进入桌面左下角,右键(Right-click)开始菜单,会出现一个巨大的各种管理快捷方式列表,找到并点击“设备管理器”。
方法 2:快速访问菜单(Method 2: Quick Access Menu)
在桌面上,按住“X”的同时按住Windows键,然后从预先填充的管理工具中选择设备管理器。

方法 3:从控制面板(Method 3: From the Control Panel)
打开控制面板(Control Panel),点击硬件(Hardware)和声音(Sound),在设备(Devices)和打印机(Printers)下,选择设备管理器(Device Manager)。
方法四:通过运行(Method 4: Via Run)
按Windows键 + R 打开运行对话框,然后在打开(Open)旁边的对话框中键入“ devmgmt.msc ”并点击确定。

方法 5:使用 Windows 搜索框(Method 5: Using the Windows search box)
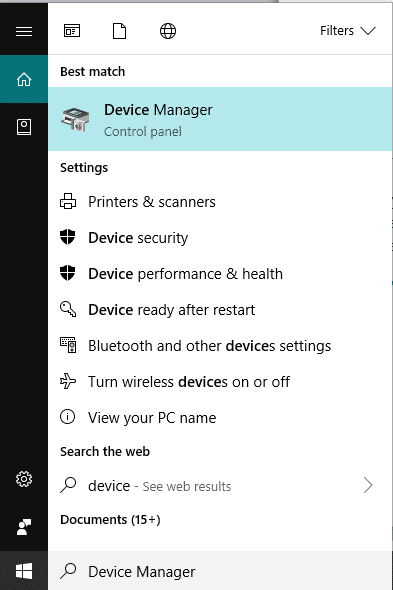
除了桌面上的windows图标外,还有一个带放大镜的图标,按下它展开搜索框,在搜索框中输入“设备管理器”并回车(Enter)。您将开始看到填充的结果,单击“最佳匹配部分”(Best Match Section)中显示的第一个结果。
方法 6:从命令提示符(Method 6: From the Command Prompt)
Windows+R热键打开“运行”(Run)对话框,输入“cmd”并点击“确定”。之后,您应该能够看到命令提示符窗口。现在,在命令提示符(Command Prompt)中,输入“(Enter ‘) start devmgmt.msc”(不带引号)并按Enter 键(Enter)。

方法七:通过 Windows PowerShell 打开设备管理器(Method 7: Open Device Manager through Windows PowerShell)
Powershell是一种更高级的命令提示符形式,用于运行任何外部程序以及自动执行命令提示符不可用的一系列系统管理任务。
要在Windows Powershell(Windows Powershell)中打开设备管理器,访问(Access)开始菜单,在所有应用程序列表中向下滚动,直到到达Windows PowerShell提示符,打开后键入“ devmgmt.msc ”并按 Enter。
这些是我们可以访问设备管理器的一些方式,根据您运行的 Windows 操作系统的版本,我们可以访问设备管理器还有很多其他独特的方式,但为了方便起见,我们将限制自己上述方法。
你如何使用设备管理器?
在我们打开设备管理器工具的那一刻,我们会看到当前安装在系统中的所有硬件组件及其软件驱动程序的列表。这些包括音频(Audio)输入和输出、蓝牙(Bluetooth)设备、显示(Display)适配器、磁盘驱动器(Disk Drives)、监视器(Monitors)、网络适配器(Network Adapter)等,这些由不同类别的外围设备分隔,可以扩展以显示当前在该类别下连接的所有硬件设备.
要进行更改或修改特定设备,请从硬件列表中选择它所属的类别,然后从显示的组件中选择所需的硬件设备。
选择设备后,会出现一个独立的对话框,该对话框显示设备的属性。
根据所选设备或硬件组件的类型,我们将看到General、Driver、Details、Events和Resources等选项卡。
现在,让我们看看每个选项卡的用途,
一般的(General)
本节提供所选硬件的简要概述,显示所选组件的名称、设备类型、该硬件设备的制造商(Manufacturer)、设备在系统中相对于它的物理位置以及设备的状态。
司机(Driver)
这是显示所选硬件组件的软件驱动程序的部分。我们可以看到驱动程序的开发者、发布日期、驱动程序版本以及驱动程序开发者的数字验证。在本节中,我们还可以看到其他与驱动程序相关的按钮,例如:
- 驱动程序详细信息:显示已安装驱动程序文件的详细信息、保存位置以及各种相关文件名。
- 更新驱动程序:此按钮可帮助我们通过在线搜索驱动程序更新或从互联网上下载的驱动程序手动更新驱动程序。
- 回滚驱动程序(Roll Back Driver):有时,某些新的驱动程序更新与我们当前的系统不兼容,或者驱动程序捆绑了某些不需要的新功能。在这些情况下,我们可能有理由回到以前工作的驱动程序版本。通过选择此按钮,我们将能够这样做。
- 禁用驱动程序:每当我们购买新系统时,它都会预装制造商认为必要的某些驱动程序。但是,由于个人用户可能由于多种原因(例如隐私)而看不到某些驱动程序的要求,因此我们可以通过按此按钮来禁用网络摄像头。
- 卸载设备:我们可以使用它来完全删除组件运行所需的驱动程序,甚至系统识别硬件组件的存在。这是一个高级选项,应谨慎使用,因为卸载某些驱动程序可能会导致操作系统(Operating System)完全失败。
细节(Details)
如果我们想控制硬件驱动程序的各个属性,我们可以在本节中进行,在这里我们可以从驱动程序的各种属性和特定属性的相应值中进行选择。这些可以稍后根据要求进行修改。
活动(Events)
安装这些软件驱动程序后,它们会指示系统定期运行大量任务。这些定时任务称为事件。此部分显示与驱动程序相关的时间戳、描述和信息。请注意,所有这些事件也可以通过事件查看器工具访问。
资源(Resources)
此选项卡显示各种资源及其设置以及设置所基于的配置。如果由于某些资源设置而导致任何设备冲突,也会在此处显示。
我们还可以通过右键单击与该类别的属性一起显示的设备类别之一来自动扫描硬件更改。
此外,我们还可以通过右键单击展开的类别列表中显示的单个设备来访问一些常规设备选项,例如更新驱动程序、禁用驱动程序、卸载设备、扫描硬件更改和设备属性。
设备(Device)管理器工具的窗口也有显示在顶部的图标。这些图标对应于我们之前已经讨论过的先前设备操作。
另请阅读:(Also Read:) Windows 10 中的管理工具是什么?(What are Administrative Tools in Windows 10?)
识别各种错误图标和代码
如果您要从本文中获取任何信息,这将是您最重要的收获。了解和识别各种错误图标将更容易找出设备冲突、硬件组件问题和设备故障。以下是这些图标的列表:
硬件无法识别(Hardware not recognized)
每当我们添加新的硬件(Hardware)外围设备时,没有支持的软件驱动程序或设备连接或插入不正确时,我们最终会看到这个图标,该图标由设备图标上方的黄色问号表示。
硬件无法正常工作(Hardware not working properly)
硬件(Hardware)设备有时会出现故障,很难知道设备何时停止正常运行。在我们开始使用该设备之前,我们可能不知道。但是,Windows 会在系统启动时尝试检查设备是否正常工作。如果Windows识别出所连接设备存在的问题,它会在黄色三角形图标上显示黑色感叹号。
禁用设备(Disabled device)
我们可能会看到这个图标,它在设备的右下方用一个向下的灰色箭头表示。IT 管理员、用户或错误可能会自动禁用设备
大多数情况下,设备管理器会显示错误代码以及相应的设备,以便我们更容易理解系统认为可能出现的问题。以下是错误代码及其说明。
|
Reason with error code |
| 1 |
This device is not configured correctly. (Error Code 1) |
| 2 |
The driver for this device might be corrupted, or your system may be running low on memory or other resources. (Error Code 3) |
| 3 |
This device cannot start. (Error Code 10) |
| 4 |
This device cannot find enough free resources that it can use. If you want to use this device, you will need to disable one of the other devices on this system. (Error Code 12) |
| 5 |
This device cannot work properly until you restart your computer. (Error Code 14) |
| 6 |
Windows cannot identify all the resources this device uses. (Error Code 16) |
| 7 |
Reinstall the drivers for this device. (Error Code 18) |
| 8 |
Windows cannot start this hardware device because its configuration information (in the registry) is incomplete or damaged. To fix this problem you should uninstall and then reinstall the hardware device. (Error Code 19) |
| 9 |
Windows is removing this device. (Error Code 21) |
| 10 |
This device is disabled. (Error Code 22) |
| 11 |
This device is not present, is not working properly, or does not have all its drivers installed. (Error Code 24) |
| 12 |
The drivers for this device are not installed. (Error Code 28) |
| 13 |
This device is disabled because the firmware of the device did not give it the required resources. (Error Code 29) |
| 14 |
This device is not working properly because Windows cannot load the drivers required for this device. (Error Code 31) |
| 15 |
A driver (service) for this device has been disabled. An alternate driver may be providing this functionality. (Error Code 32) |
| 16 |
Windows cannot determine which resources are required for this device. (Error Code 33) |
| 17 |
Windows cannot determine the settings for this device. Consult the documentation that came with this device and use the Resource tab to set the configuration. (Error Code 34) |
| 18 |
Your computer’s system firmware does not include enough information to properly configure and use this device. To use this device, contact your computer manufacturer to obtain a firmware or BIOS update. (Error Code 35) |
| 19 |
This device is requesting a PCI interrupt but is configured for an ISA interrupt (or vice versa). Please use the computer’s system setup program to reconfigure the interrupt for this device. (Error Code 36) |
| 20 |
Windows cannot initialize the device driver for this hardware. (Error Code 37) |
| 21 |
Windows cannot load the device driver for this hardware because a previous instance of the device driver is still in memory. (Error Code 38) |
| 22 |
Windows cannot load the device driver for this hardware. The driver may be corrupted or missing. (Error Code 39) |
| 23 |
Windows cannot access this hardware because its service key information in the registry is missing or recorded incorrectly. (Error Code 40) |
| 24 |
Windows successfully loaded the device driver for this hardware but cannot find the hardware device. (Error Code 41) |
| 25 |
Windows cannot load the device driver for this hardware because there is a duplicate device already running in the system. (Error Code 42) |
| 26 |
Windows has stopped this device because it has reported problems. (Error Code 43) |
| 27 |
An application or service has shut down this hardware device. (Error Code 44) |
| 28 |
Currently, this hardware device is not connected to the computer. (Error Code 45) |
| 29 |
Windows cannot gain access to this hardware device because the operating system is in the process of shutting down. (Error Code 46) |
| 30 |
Windows cannot use this hardware device because it has been prepared for safe removal, but it has not been removed from the computer. (Error Code 47) |
| 31 |
The software for this device has been blocked from starting because it is known to have problems with Windows. Contact the hardware vendor for a new driver. (Error Code 48) |
| 32 |
Windows cannot start new hardware devices because the system hive is too large (exceeds the Registry Size Limit). (Error Code 49) |
| 33 |
Windows cannot verify the digital signature for the drivers required for this device. A recent hardware or software change might have installed a file that is signed incorrectly or damaged, or that might be malicious software from an unknown source. (Error Code 52) |
How to Switch to OpenDNS or Google DNS on Windows
结论
随着操作系统技术的不断改进,它对于设备管理的单一来源变得很重要。开发设备(Device)管理器是为了让操作系统了解物理变化并跟踪它们随着越来越多的外围设备的添加而发生的变化。了解硬件何时出现故障并需要立即关注将在短期和长期内帮助个人和机构。
What is Device Manager? [EXPLAINED]
The Windows operating system currently holds a 96% market share in the world of personal computers. To capitalize on this opportunity, hardware manufacturers try and create products that add a lot of features to the existing computer builds.
But none of this is standardized. Every manufacturer works with its own software features which are closed source to distinguish themselves from their competitors.
If every hardware is different, how will the operating system know how to use the hardware?
This is taken care of by the device drivers. Since Windows cannot build support for all the hardware devices on the planet, they left it up to the hardware manufacturers to develop compatible drivers.
The Windows Operating System only offers us an interface to interact with the installed devices and drivers on the system. This interface is called the Device Manager.

What is a Device Manager?
It is a software component of the Microsoft Windows operating system, which is like a command center of all the hardware peripherals connected to the system. The way it works is by giving us a brief and organized overview of all the windows approved hardware devices that are operating in the computer.
This could be electronic components such as keyboard, mouse, monitors, hard disk drives, processors, etc. It is an administrative tool that is a part of the Microsoft Management Console.
Device Manager comes preloaded with the operating system, however, there are other third-party programs available in the market that can be used to achieve the same desired results but it is encouraged not to install these third-party applications due to the inherent security risks they possess.
Microsoft started bundling this tool with the operating system with the introduction of Windows 95. Initially, it was just designed to display and interact with pre-existing hardware. Over the next few revisions, the hot-plugging capability was added, which enables the kernel to notify the device manager of any new hardware-related changes that are taking place. Such as plugging in a USB thumb drive, insertion of a new network cable, etc.
Device Manager helps us to:
- Modify hardware configuration.
- Change and retrieve hardware drivers.
- Detecting conflicts between the hardware devices that are plugged into the system.
- Identify problematic drivers and disable them.
- Display the hardware information such as the device manufacturer, model number, classification device, and more.
Why Do We Need a Device Manager?
There are a lot of reasons why we might need a device manager, but the most important reason we need the device manager is for software drivers.
A software driver is as Microsoft defines software that allows your computer to communicate with hardware or devices. But why do we need that, so let’s say you’ve got a sound card you should be able to just plug it in with no drivers and your music player should generate a digital signal that the sound card should make.
That’s basically how it would have worked if there was only one sound card in existence. But the real problem is that there are literally thousands of sound devices and all of them will work completely differently from each other.
And for everything to work correctly software makers would need to rewrite their software with specialized signaling for your sound card along with every card that ever existed and every card that ever will exist.
So a software driver acts as an abstraction layer or translator in a way, where the software programs only have to interact with your hardware in one standardized language and the driver handles the rest.
Also Read: What is Fragmentation and Defragmentation
Why do drivers cause so many issues?
Our hardware devices come with a lot of capabilities that the system needs to interact in a particular way. Even though standards exist to help the hardware manufacturers to make the perfect driver. There are other devices and other pieces of software that can cause conflicts. Also, there are separate drivers that need to be maintained for multiple operating systems like Linux, Windows, and others.
Each with its own universal language that the driver needs to translate to it. This leaves plenty of room for one of the variants of a driver for a particular piece of hardware to have an imperfection or two.
How to Access the Device Manager?
There are various ways by which we can access the device manager, in most of the versions of Microsoft windows we can open device manager from the command prompt, the control panel, from the run tool, right-clicking the start menu, etc.
Method 1: From the start menu
Go to the lower left side of the desktop, Right-click on the start menu, a huge list of various administrative shortcuts will appear, locate and click on the “device manager”.
Method 2: Quick Access Menu
On the desktop, keep holding the Windows key while you press ‘X’, then select the device manager from the pre-populated administrative tools.

Method 3: From the Control Panel
Open the Control Panel, click on Hardware and Sound, under the Devices and Printers, select Device Manager.
Method 4: Via Run
Press Windows key + R to open the run dialog box, then in the dialog box besides Open type “devmgmt.msc” and tap OK.

Method 5: Using the Windows search box
Besides the windows icon in the desktop, there is an icon with a magnifying glass, press that to expand the search box, in the search box type “Device Manager” and hit Enter. You will start to see the results populate, click on the first result that is displayed in the Best Match Section.

Method 6: From the Command Prompt
Open the Run dialog using Windows+R hotkeys, enter ‘cmd’ and tap OK. After that, you should be able to see the command prompt window. Now, in the Command Prompt, Enter ‘start devmgmt.msc’ (without quotes) and hit Enter.

Method 7: Open Device Manager through Windows PowerShell
Powershell is a more advanced form of command prompt which is used to run any external programs as well as automate an array of system administration tasks not available to the command prompt.
To open the device manager in Windows Powershell, Access the start menu, scroll down in the all applications list till you reach Windows PowerShell prompt, Once opened type ‘devmgmt.msc‘ and press Enter.
These are some of the ways we can access the device manager, there are plenty of other unique ways we can access the device manager depending on the version of windows operating system you are running, but for the sake of convenience, we will limit ourselves to the above-mentioned methods.
How do you put the device manager to use?
The moment we open the device manager tool we are greeted with a list of all the hardware components and their software drivers that are currently installed in the system. These include Audio inputs and outputs, Bluetooth devices, Display adapters, Disk Drives, Monitors, Network Adapter, and more, these are separated by different categories of peripherals, which can be expanded to display all the hardware devices that are currently connected under that category.
To make changes or to modify a particular device, from the hardware list select the category it falls under, then from the displayed components choose the desired hardware device.
Upon selecting the device, an independent dialog box appears, this box displays the properties of the device.
Depending on the type of device or hardware component selected, we will see tabs such as General, Driver, Details, Events, and Resources.
Now, let’s see what each of these tabs can be used for,
General
This section provides a brief overview of the hardware selected, that displays the name of the component selected, the type of device it is, the Manufacturer of that hardware device, the physical location of the device in the system that is relative to it and the status of the device.
Driver
This is the section that displays the software driver for the selected hardware component. We get to see the developer of the driver, the date it got released, the driver version, and the digital verification of the driver developer. In this section, we also get to see other driver-related buttons such as:
- Driver details: This displays the details of the driver files that have been installed, the location where they have been saved and various dependent file names.
- Update driver: This button helps us manually update the driver by either searching for the driver update online or driver that has been downloaded from the internet.
- Roll Back Driver: Sometimes, certain new driver updates are not compatible with our current system or there are certain new features that are not required that have been bundled with the driver. In these situations, we may have a reason to go back to a previously working version of the driver. By selecting this button we will be able to do so.
- Disable driver: Whenever we buy a new system, it comes preloaded with certain drivers that the manufacturer deems necessary. However, as an individual user may not see the requirement of certain drivers due to any number of reasons say privacy then we can disable the webcam by pressing this button.
- Uninstall device: We can use this to completely remove the drivers necessary for the component to function or even the system to recognize the existence of the hardware component. This is an advanced option, which should be used with caution as uninstalling certain drivers may lead to total Operating System failure.
Details
If we want to control individual properties of a hardware driver, we can do so in this section, here we get to select from various properties of the driver and a corresponding value for a particular property. These can be later modified based on the requirement.
Events
Upon installing these software drivers, they instruct the system to run a plethora of tasks periodically. These timed tasks are called events. This section displays the timestamp, description, and information associated with the driver. Do note that all of these events can also be accessed via the event viewer tool.
Resources
This tab displays various resources and their setting and the configuration the settings are based on. If there are any device conflicts due to certain resource settings that will also be displayed here.
We can also automatically scan for hardware changes by right-clicking on one of the device categories that are displayed along with the properties of that category.
Additionally, we can also access some of the general device options such as update driver, disable driver, uninstall devices, scan for hardware changes, and device properties by right-clicking on the individual device shown in the expanded category list.
The Device manager tool’s window also has icons that are displayed on the top. These icons correspond to the previous device actions that we have already discussed earlier.
Also Read: What are Administrative Tools in Windows 10?
Identification of various error icons and codes
If you were to take any information from this article with you, this would be the most important takeaway for you. Understanding and identifying various error icons will make it easier to figure out the device conflicts, issues with hardware components, and malfunctioning devices. Here’s a list of those icons:
Hardware not recognized
Whenever we add a new Hardware peripheral, without a supporting software driver or when the device is improperly connected or plugged, we will end up seeing this icon which is denoted by a yellow question mark over the device icon.
Hardware not working properly
Hardware devices sometimes tend to malfunction, it is quite hard to know when a device has stopped functioning as it should. We may not know until we start to use that device. However, windows will try to check if a device is functioning or no, while the system is booting. If Windows recognizes the problem which the connected device has it shows a black exclamation on a yellow triangle icon.
Disabled device
We may see this icon which is denoted by a grey arrow pointing down in the lower right side of the device. A device could be automatically be disabled by the IT administrator, by a user, or maybe by mistake
Most of the time the device manager displays the error code along with the corresponding device, to make it easier for us to make sense of what does the system thinks of what could be going wrong. Following is the error code along with the explanation.
|
Reason with error code |
| 1 |
This device is not configured correctly. (Error Code 1) |
| 2 |
The driver for this device might be corrupted, or your system may be running low on memory or other resources. (Error Code 3) |
| 3 |
This device cannot start. (Error Code 10) |
| 4 |
This device cannot find enough free resources that it can use. If you want to use this device, you will need to disable one of the other devices on this system. (Error Code 12) |
| 5 |
This device cannot work properly until you restart your computer. (Error Code 14) |
| 6 |
Windows cannot identify all the resources this device uses. (Error Code 16) |
| 7 |
Reinstall the drivers for this device. (Error Code 18) |
| 8 |
Windows cannot start this hardware device because its configuration information (in the registry) is incomplete or damaged. To fix this problem you should uninstall and then reinstall the hardware device. (Error Code 19) |
| 9 |
Windows is removing this device. (Error Code 21) |
| 10 |
This device is disabled. (Error Code 22) |
| 11 |
This device is not present, is not working properly, or does not have all its drivers installed. (Error Code 24) |
| 12 |
The drivers for this device are not installed. (Error Code 28) |
| 13 |
This device is disabled because the firmware of the device did not give it the required resources. (Error Code 29) |
| 14 |
This device is not working properly because Windows cannot load the drivers required for this device. (Error Code 31) |
| 15 |
A driver (service) for this device has been disabled. An alternate driver may be providing this functionality. (Error Code 32) |
| 16 |
Windows cannot determine which resources are required for this device. (Error Code 33) |
| 17 |
Windows cannot determine the settings for this device. Consult the documentation that came with this device and use the Resource tab to set the configuration. (Error Code 34) |
| 18 |
Your computer’s system firmware does not include enough information to properly configure and use this device. To use this device, contact your computer manufacturer to obtain a firmware or BIOS update. (Error Code 35) |
| 19 |
This device is requesting a PCI interrupt but is configured for an ISA interrupt (or vice versa). Please use the computer’s system setup program to reconfigure the interrupt for this device. (Error Code 36) |
| 20 |
Windows cannot initialize the device driver for this hardware. (Error Code 37) |
| 21 |
Windows cannot load the device driver for this hardware because a previous instance of the device driver is still in memory. (Error Code 38) |
| 22 |
Windows cannot load the device driver for this hardware. The driver may be corrupted or missing. (Error Code 39) |
| 23 |
Windows cannot access this hardware because its service key information in the registry is missing or recorded incorrectly. (Error Code 40) |
| 24 |
Windows successfully loaded the device driver for this hardware but cannot find the hardware device. (Error Code 41) |
| 25 |
Windows cannot load the device driver for this hardware because there is a duplicate device already running in the system. (Error Code 42) |
| 26 |
Windows has stopped this device because it has reported problems. (Error Code 43) |
| 27 |
An application or service has shut down this hardware device. (Error Code 44) |
| 28 |
Currently, this hardware device is not connected to the computer. (Error Code 45) |
| 29 |
Windows cannot gain access to this hardware device because the operating system is in the process of shutting down. (Error Code 46) |
| 30 |
Windows cannot use this hardware device because it has been prepared for safe removal, but it has not been removed from the computer. (Error Code 47) |
| 31 |
The software for this device has been blocked from starting because it is known to have problems with Windows. Contact the hardware vendor for a new driver. (Error Code 48) |
| 32 |
Windows cannot start new hardware devices because the system hive is too large (exceeds the Registry Size Limit). (Error Code 49) |
| 33 |
Windows cannot verify the digital signature for the drivers required for this device. A recent hardware or software change might have installed a file that is signed incorrectly or damaged, or that might be malicious software from an unknown source. (Error Code 52) |
How to Switch to OpenDNS or Google DNS on Windows
Conclusion
As the technologies of the Operating systems kept improving it became important for a singular source of device administration. The Device manager was developed to make the operating system aware of the physical changes and keep a track of the mas they take place as more and more peripherals are being added. Knowing when the hardware is malfunctioning and requiring immediate attention would help individuals and institutions alike in a short as well as long run.





