您有新的数码单反相机(DSLR camera)、运动相机(action camera)或新的智能手机吗?是否要为其添加存储卡(memory card)?您(Are)想知道如何选择合适的存储卡(memory card)吗?在您这样做之前,您需要了解有哪些不同类型的存储卡(memory card),以及哪些适合您的特定设备。阅读这篇文章,了解目前最常用的存储卡(memory card),它们的名称是什么意思,速度等级(Speed Class)是什么,等等:
什么是存储卡?
存储卡是设计用于存储信息的小型电子设备。(Memory cards are small electronic devices designed to store information.)它们通常使用闪存,就像USB 记忆(USB memory)棒或固态驱动器一样。存储卡用于数码相机、智能手机、平板电脑、媒体播放器、笔记本电脑、移动控制台、监控摄像头,甚至一些台式电脑。因为他们使用闪存,所以当您拔下存储卡时,存储卡(memory card)上保存的信息不会丢失。这也意味着您可以随时复制、移动和删除文件,以及(you can copy, move, and delete files, as well as)格式化存储卡。
与USB 闪存(USB flash)驱动器不同,对于存储卡,您无需使用USB 端口(USB port)将它们插入其他设备。相反,存储卡通过支持它们的设备上可用的特殊硬件接口(称为插槽(slots))直接连接。

有多少种不同类型的存储卡?
几十年前,有许多不同类型的存储卡(memory card)可供使用,由许多硬件制造商创建。尽管许多公司试图制定自己的存储卡(memory card)标准,但只有少数公司能够在竞争中获胜。今天,大多数存储卡(memory card)属于两个主要系列之一:安全数字(Secure Digital)和CompactFlash。让我们看看他们每个人都提供了什么:

SD卡有哪些不同类型?
Secure Digital以其SD首字母缩写而闻名,包括许多不同类型的 SD 卡,具有不同的形状和大小:
- SD(安全数字)(SD (Secure Digital)) - 一种旧类型的存储卡(memory card),存储容量高达 2 GB,默认格式化为FAT16。SD 卡的物理尺寸为32 × 24 × 2.1 mm。此尺寸已成为所有其他较新版本 SD 卡的标准,例如SDHC、SDXC或SDUC。如今(Nowadays),许多人也使用术语 SD 来指代较新的SDHC、SDXC或SDUC 存储(SDUC memory)卡。
- microSD是 SD 卡的小型化版本,标准尺寸为15 × 11 × 1 mm。microSD 也是一种老式的存储卡(memory card),最大存储容量(storage capacity)为 2 GB。新版本的 microSDHC、microSDXC 和 microSDUC 卡保留了它们的物理尺寸。此外,人们将这些卡称为 microSD 卡,尽管这在技术上并不正确。
- miniSD 卡比普通(miniSD)SD 卡小,但比 microSD 卡大:21.5 × 20 × 1.4 mm。否则,它们的存储容量范围(storage capacity range)与SD/microSD卡相同。
- SDHC(安全数字高容量)(SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity))卡在大小、尺寸和速度方面与 SD 相同,但存储容量(storage capacity)范围在 2 GB 到 32 GB 之间。此外,SDHC卡默认格式化为FAT32。
- microSDHC是SDHC的小型化版本。micro SDHC卡还可以存储多达 32 GB 的数据。
- miniSDHC卡的体型(body size)与 miniSD 卡相同,但规格与SDHC相同,最大存储容量(storage size)为 32 GB。
- SDXC(安全数字扩展容量)(SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity))是SDHC的改进版本。在保持与 SD 相同的物理特性的同时,SDXC卡最多可容纳 2 TB 的文件,并且还提供更快的数据传输速度。默认情况下, SDXC(SDXC)卡使用exFAT 文件系统(exFAT file system)进行格式化。
- microSDXC卡的物理尺寸与microSD 和 microSDHC 卡(microSD and microSDHC cards)相同,但速度更快,理论上存储容量(storage capacity)可达 2 TB。
- SDUC(安全数字超容量)卡保留了与(SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity))SD/SDHC/SDXC卡相同的物理构造,但它们的最大存储容量(storage capacity)要大得多,理论上最大为 128 TB。默认情况下,SDUC卡使用 exFAT 进行格式化。
- microSDUC是 SDUC 的小型化版本(SDUC)。它们具有与 microSD/microSDHC/microSDXC 卡相同的尺寸,但在速度和存储空间(speed and storage space)方面具有常规SDUC卡的所有优势。
为了帮助您理解所有这些数据,请查看下面的比较:
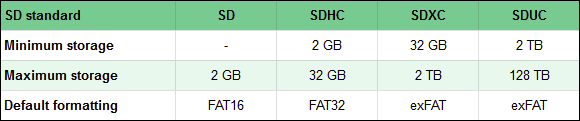
您可能已经从列表中注意到,我们没有提到miniSDXC 或 miniSDUC 卡(miniSDXC or miniSDUC cards)。那是因为这种尺寸格式(size format)已经被放弃了,市场上也没有这样的存储卡。

SD存储(SD memory)卡有多快,卡速度等级是什么意思(class mean)?
当提到SD 卡(SD card)的速度时,您在其上看到的评级和分类指的是顺序读取和/或写入速度。当您查看SD 卡(SD card)的广告速度时,要考虑的主要因素是其总线的速度。例如,在某些SD 卡(SD card)上,您可能会看到其制造商印制的UHS 或 UHS-II之类的东西。(UHS or UHS-II)

此信息可以帮助您了解SD 卡(SD card)在正常情况下的额定速度。目前SD卡(SD card)上常用的总线有:
- 默认(Default) 总线速度(bus speed)意味着具有此等级(或根本没有等级)的SD 卡(SD card)可以以高达 12.5 MB/s读取和写入数据。
- 高速 (HS)(High Speed (HS))提供两倍的默认速度 - 25 MB/s用于在SD 卡(SD card)上读取和写入数据。
- UHS-I (Ultra High Speed I) SD 卡在双向传输数据时可达到 50 MB/s(全双工)的读/写速度,在单向传输数据时可达到 104 MB/s (一半-双工,读或写)。
- UHS-II(超高速 II)(UHS-II (Ultra High-Speed II))将读/写速度提高到全双工156 MB/sMB/s。
- UHS-III(超高速 III)(UHS-III (Ultra High Speed III))甚至更高,在全双工模式下达到 312 MB/s,在半双工模式下达到 624 MB/s。
UHS总线仅适用于SDHC、SDXC、SDUC卡及其微型变体。第一代 SD 卡不支持UHS总线。(UHS)

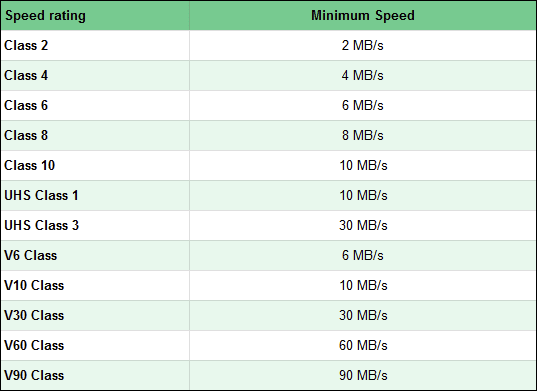
决定SD 卡(SD card)读写速度的第二个重要因素是其等级(Class rating)。该评级告诉我们存储卡(memory card)的最低持续速度,以每秒传输的兆字节数为单位。SD Class 等级(Class rating)分为三个不同的类别:
- 速度等级(Speed Class)用于SDHC 存储(SDHC memory)卡,可以等于 2、4、6、8 或 10。每个数字告诉您以MB/s表示的最低速度。例如,速度等级(Speed Class)2 表示存储卡(memory card)的最低持续速度为 2 MB/s。Class 10 (A Class 10) SD 卡(SD card)的最低速度为 10 MB/s,依此类推。
- UHS 速度等级(UHS Speed Class)是用于使用UHS 总线的(UHS bus)SDHC 和 SDXC 存储卡的(SDHC and SDXC memory cards)速度等级(speed rating)。UHS 速度等级(UHS Speed Classes)可以具有以下两个值之一:1 或 3。具有UHS 等级 1的(UHS Class 1)存储卡(memory card)意味着其最低速度等于 10 MB/s,而UHS 等级 3(UHS Class 3)卡的最低速度为 30 MB/s。
- 视频速度等级(Video Speed Class),或简称为V 等级(V Class),用作设计用于视频录制设备的存储卡的等级。此评级可确保您的卡可以支持录制视频所需的最低速度。有五种V 等级(V Class):V6、V10、V30、V60和V90。V(V tell)之后的数字告诉您该卡的最低持续速度。例如,V10表示该卡在最坏情况下的传输速度(transfer speed)至少为 10 MB/sV60的工作速度最低为 60 MB/s,以此类推。
要总结速度差异,请看下表:
SD 卡最常见的用例之一是为视频录制提供存储空间(storage space)。无论您使用摄像机(video camera)、运动(action cam)相机,甚至是智能手机,仅仅购买一张有足够空间用于录制的存储卡是不够的。(memory card)您还应该仔细查看该存储卡(memory card)的速度,以确保它可以以您喜欢的分辨率处理视频录制。阅读下表,您可以在其中查看您的卡对于不同类型的视频录制场景应具有的速度等级:(Speed)

什么是 Compact Flash,谁在使用CF 存储(CF memory)卡?
CompactFlash以其首字母缩略词CF为许多人所知,是一种主要用于专业和高端数码照片和摄像机的(photo and video cameras)存储卡(memory card)格式。佳能和尼康(Canon and Nikon)是选择在其电子设备上使用CompactFlash的公司之一。(CompactFlash)
过去,CF 卡的存储容量和数据传输速度都比其他类型的存储卡要快。这就是照片和视频专业人士(photo and video professionals)首选 CompactFlash 卡的原因。一些人也更喜欢 CF 卡,因为它们的物理尺寸更大,这使得它们更容易处理,也更难丢失。
由于其较大的存储容量(storage capacity)和较快的速度,CompactFlash卡在市场上占有一席之地,并且至今仍在使用和使用。有两种类型的 CF 卡:
- CompactFlash I卡的存储容量高达 128 PB(目前现实世界(world right)中可用的最大容量为 512 GB),标准物理尺寸为 43 × 36 × 3.3 mm。
- CompactFlash II卡的规格与 Type I 相同,但更厚:43 × 36 × 5 mm。

CompactFlash已被CFexpress取代,CFexpress是一种速度非常快的存储卡,因为它们使用PCI Express 3.0并支持NVMe。不幸的是,CFexpress卡不向后兼容 CF 插槽,因为它们具有不同的物理尺寸 (38.5 × 29.8 × 3.8 mm) 并使用更新的技术。
您还有其他关于存储卡的问题吗?
我们希望本文对您有所帮助,并且您现在可以更好地掌握不同类型的存储卡。在结束之前,请告诉我们您是否对存储卡有任何其他问题。您对我们的指南有什么要补充的吗?使用下面的评论部分让我们知道。
What are the different types of memory cards? What do their specs mean?
Dо you have a new DSLR camera, an action camera, or maybе a new smartphone? Dо you wаnt to add a memory card to it? Are yoυ wondering how to choose the right memory cаrd? Befоrе you do that, you need to understand what are the different types of memory cards out there, and which fits your specific device. Read this article tо see the most common memory cards used right now, what their names mean, what Speed Class ratings are, and more:
What is a memory card?
Memory cards are small electronic devices designed to store information. They typically use flash memory, just like USB memory sticks or solid-state drives. Memory cards are used inside digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, media players, laptops, mobile consoles, surveillance cameras, and even in some desktop computers. Because they use flash memory, the information saved on a memory card is not lost when you unplug it. It also means that you can copy, move, and delete files, as well as format memory cards whenever you want.
Unlike USB flash drives, for memory cards, you don't use a USB port to plug them into other devices. Instead, memory cards directly connect via special hardware interfaces, called slots, available on the devices that support them.

How many different types of memory cards are there?
Decades ago, there were many different types of memory cards available, created by many hardware manufacturers. Although many companies tried to set their own memory card standards, only a few have managed to win the competition. Today, most memory cards are part of one of the two main families: Secure Digital and CompactFlash. Let's see what each of them has to offer:

What are the different types of SD cards?
Secure Digital, better known by its SD acronym, includes many different types of SD cards, with different shapes and sizes:
- SD (Secure Digital) - an old type of memory card that has storage capacities up to 2 GB, formatted by default in FAT16. SD cards have a physical size of 32 × 24 × 2.1 mm. This size has become the norm for all the other, newer versions of SD cards, such as SDHC, SDXC, or SDUC. Nowadays, many people are using the term SD to refer to the newer SDHC, SDXC, or SDUC memory cards too.
- microSD are miniaturized versions of SD cards, which have a standard size of 15 × 11 × 1 mm. microSD is also an old type of memory card, with a maximum storage capacity of 2 GB. Their physical size was kept for the newer versions of microSDHC, microSDXC, and microSDUC cards. Also, people refer to these cards as microSD cards, although that is not technically correct.
- miniSD cards are smaller than regular SD cards but larger than microSD cards: 21.5 × 20 × 1.4 mm. Otherwise, they have the same storage capacity range as SD/microSD cards.
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) cards are identical to SD in terms of size, dimensions, and speed, but have a range of storage capacity between 2 GB and 32 GB. Also, SDHC cards are formatted by default in FAT32.
- microSDHC is the miniaturized version of SDHC. microSDHC cards can also store up to 32 GB of data on them.
- miniSDHC cards have the same body size as miniSD cards, but the same specs as SDHC, with a storage size of up to 32 GB.
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity) is an improved version of SDHC. While keeping the same physical aspects as SD, SDXC cards can hold up to 2 TB of files, and also provide faster data transfer speeds. SDXC cards are formatted, by default, using the exFAT file system.
- microSDXC cards have the same physical size as microSD and microSDHC cards, but they're faster, and their storage capacity can theoretically go up to 2 TB.
- SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity) cards retain the same physical build of SD/SDHC/SDXC cards, but their maximum storage capacity is much greater, with a theoretical maximum of 128 TB. By default, SDUC cards come formatted using exFAT.
- microSDUC is the miniaturized version of SDUC. They have the same size as microSD/microSDHC/microSDXC cards, but all the benefits in speed and storage space of regular SDUC cards.
To help you make sense of all this data, take a look at the comparison below:

As you might have noticed from the list, we did not mention miniSDXC or miniSDUC cards. That's because this size format has been abandoned, and there are no such memory cards available on the market.

How fast are SD memory cards, and what does card speed class mean?
When referring to the speed of SD cards, the ratings and classifications you see on them refer to the sequential read and/or write speeds. The main factor to take into consideration when you're looking at the advertised speeds of an SD card is how fast its bus is. For example, on some SD cards, you might see things such as UHS or UHS-II printed by their manufacturers.

This information can help you understand how fast an SD card is rated to be, under normal conditions. The commonly used buses on SD cards nowadays are:
- Default bus speed means that the SD card with this rating (or no rating at all) can read and write data at up to 12.5 MB/s.
- High Speed (HS) offers double the default speed - 25 MB/s for both reading and writing data on the SD card.
- UHS-I (Ultra High Speed I) SD cards can reach a read/write speed of 50 MB/s (full-duplex) when data is transferred both ways and up to 104 MB/s when data is transferred one way only (half-duplex, read or write).
- UHS-II (Ultra High-Speed II) increases the read/write speeds up to 156 MB/s in full-duplex and 312 MB/s in half-duplex.
- UHS-III (Ultra High Speed III) goes even higher, reaching 312 MB/s in full-duplex mode and 624 MB/s in half-duplex mode.
The UHS buses are only found on SDHC, SDXC, SDUC cards, and their micro variants. UHS buses are not supported by first generation SD cards.

The second important factor in determining the read and write speeds of an SD card is its Class rating. This rating tells us the minimum sustained speed of a memory card, measured in transferred megabytes per second. SD Class ratings are divided into three different categories:
- Speed Class is used for SDHC memory cards and can be equal to 2, 4, 6, 8, or 10. Each number tells you the minimum speed expressed in MB/s. For example, a Speed Class of 2 means that the memory card has a minimum sustained speed of 2 MB/s. A Class 10 SD card has a minimum speed of 10 MB/s, and so on.
- UHS Speed Class is a speed rating used for SDHC and SDXC memory cards that use a UHS bus. The UHS Speed Classes can have one of two values: 1 or 3. A memory card with UHS Class 1 means its minimum speed is equal to 10 MB/s, while a UHS Class 3 card has a minimum speed of 30 MB/s.
- Video Speed Class, or V Class in short, is used as a rating for memory cards designed to work with video recording devices. This rating assures you that a card can support the minimum speeds needed for recording video. There are five V Classes: V6, V10, V30, V60, and V90. The numbers that come after V tell you the minimum sustained speed of the card. For example, V10 means that the card has a transfer speed of at least 10 MB/s in the worst scenario, V60 works at a minimum speed of 60 MB/s, and so on.
To summarize the speed differences, take a look at the table below:

One of the most common use cases for SD cards is for providing storage space for video recordings. Whether you use a video camera, an action cam, or even a smartphone, it is not enough to just buy a memory card with a lot of space for your recordings. You should also take a good look at how fast that memory card is, to make sure that it can handle video recording in the resolution you prefer. Read the table below, where you can see what Speed Classes your card should have for different types of video recording scenarios:

What is Compact Flash and who's using CF memory cards?
CompactFlash, known by many under its acronym CF, is a memory card format that's mainly used in professional and high-end digital photo and video cameras. Canon and Nikon are among the companies that choose to use CompactFlash on their electronic devices.
In the past, CF cards used to offer both larger storage capacities and faster data transfer speeds than other types of memory cards did. That's why CompactFlash cards were preferred by photo and video professionals. Some also liked CF cards more because of their bigger physical size, which made them easier to handle and harder to lose.
Because of their larger storage capacity, as well as their fast speeds, CompactFlash cards have held well on the market and are still used and available today. There are two types of CF cards:
- CompactFlash I cards have storage capacities that can go up to 128 PB (maximum available in the real world right now is 512 GB) and a standard physical size of 43 × 36 × 3.3 mm.
- CompactFlash II cards have the same specs as Type I but are thicker: 43 × 36 × 5 mm.

CompactFlash has been superseded by CFexpress, a type of memory cards that can be incredibly fast, as they're using PCI Express 3.0 and support NVMe. Unfortunately, CFexpress cards are not backward compatible with CF slots, as they have both different physical sizes (38.5 × 29.8 × 3.8 mm) and use newer technologies.
Do you have any other questions about memory cards?
We hope that this article has been helpful and that you now have a better grasp of the different types of memory cards. Before closing, tell us if you have any other questions about memory cards. Do you have anything to add to our guide? Use the comments section below to let us know.









