文件资源管理器是(File Explorer)Windows设备上的默认文件管理工具。与Windows(Windows)上的所有其他系统进程一样,文件资源管理器(File Explorer)也偶尔会出现故障。如果您发现Windows 资源管理器(Explorer)在使用过程中没有响应,您可以尝试一些方法。
我们编写了一份综合指南,涵盖了当 Windows 资源管理器不断崩溃时要遵循的提示(tips to follow when Windows Explorer keeps crashing)。在本文中,我们将通过九个修复来尝试当您启动文件资源管理器(File Explorer)时,它会继续加载或无法打开文件和文件夹。
1.修改PC的显示布局
对于Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)没有响应,这是一个相当奇怪但有效的解决方案。显然,使用不推荐的屏幕布局和分辨率可能会导致文件资源管理器(File Explorer)出现故障。
检查您 PC 的显示设置,并确保您使用的是推荐的比例/布局。转到“设置”(Settings ) > “系统( System )” > “显示”( Display)并确保将文本、应用程序和其他项目(size of text, apps, and other items)的大小设置为100%Windows推荐的任何选项。

如果您的 PC 的显示比例已设置为 100%,请尝试将其更改为 125%,然后再重新设置为 100%。
2.杀死(Kill)并重新启动(Restart)文件资源管理器(File Explorer)
如果更改 PC 的分辨率后Windows 资源管理器仍然没有响应,请终止(Windows Explorer)Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)进程并重新启动它。有几种方法可以重新启动Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer):
使用任务管理器(Using Task Manager)
启动Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)(按Ctrl + Shift + Esc),右键单击应用程序部分中的Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer),然后单击结束任务(End Task)以终止文件资源管理器。

通过单击任务栏中的文件夹图标重新启动Windows 资源管理器。(Windows Explorer)或者,使用任务管理器(Task Manager):单击菜单栏上的文件并选择(File)运行新任务(Run new task)。

在对话框中键入explorer.exe并单击(explorer.exe)OK。

这将立即启动Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)。现在继续检查您是否可以在文件资源管理器(File Explorer)中访问您的文件和文件夹而没有任何延迟。
使用命令提示符(Using Command Prompt)
您还可以使用命令提示(Command Prompt)实用程序来终止和重新启动Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)。右键单击(Right-click)Windows图标(Windows),然后从快速访问(Quick Access)菜单中选择命令提示符(Command Prompt)( Admin ) 。在控制台输入taskkill /f /im explorer.exe回车(Enter)。

当您终止Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)时,您的 PC 的任务栏和桌面图标将消失。这是正常的,只是暂时的。要重新启动文件资源管理器(File Explorer),请在命令提示符(Command Prompt)窗口中输入start explorer.exe ,然后按(start explorer.exe)Enter继续。

使用 BAT 文件重新启动文件资源管理器(Restart File Explorer Using A BAT File)
BAT 文件可(BAT files)让您轻松地自动执行任务和操作。如果文件资源管理器(File Explorer)经常无法响应并且重新启动进程通常可以解决问题,您应该创建一个BAT文件,专门用于单击按钮重新启动文件资源管理器。(File Explorer)
- 右键单击(Right-click)桌面上的空白区域。单击(Click) 新建(New),然后选择文本文档(Text Document)。

- 将文档命名为Restart Explorer并按Enter。

- 双击(Double-click)新创建的文件以使用记事本(Notepad)打开。
- 将以下命令粘贴到文档中:
taskkill /f /IM explorer.exe
启动 explorer.exe(start explorer.exe)
退出(exit)

- 单击菜单栏中的文件,然后选择(File)另存为(Save As)。

- 在文件(FIle)名对话框中,重命名文件Restart Explorer.bat并确保将保存类型(Save as type)选项设置为所有文件(All Files)。

- 单击保存(Save)以继续。
要使用新创建的BAT文件重新启动Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer),请返回桌面(Desktop),右键单击该文件,然后选择以管理员身份运行(Run as administrator)。

Windows将通过命令提示符运行(Command Prompt)BAT文件中的命令并重新启动Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)。
3.检查损坏的系统文件
当某些系统文件损坏、丢失或损坏时,某些核心Windows功能(如文件资源管理器(File Explorer))可能会开始出现故障。值得庆幸的是,这很容易解决。系统文件检查器(System File Checker)将扫描您的 PC 以查找损坏或丢失的系统文件(scan your PC for corrupt or missing system files),并相应地修复或替换它们。
请按照以下步骤在Windows 10 计算机上运行系统文件检查器。(System File Checker)
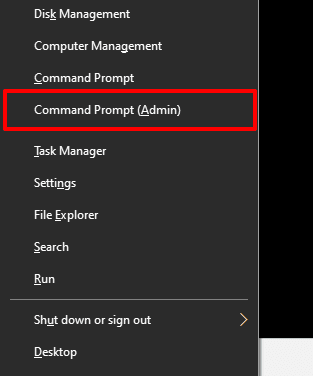
1. 右键单击开始(Start)菜单图标并选择命令提示符(管理员)(Command Prompt (Admin))。
2. 在命令提示符(Command Prompt)控制台中键入或粘贴以下命令,然后按Enter。
sfc /scannow

如果在命令提示符(Command Prompt)执行完命令后Windows 文件资源管理器(Windows File Explorer)仍然没有响应,请重新启动计算机并重试。
4.清除文件资源管理器历史
Windows 文件资源管理器(Windows File Explorer)会记录所有以前的操作和活动——最近访问的文件和文件夹、搜索、地址栏条目等。当实用程序的历史累积到某个点时,Windows 文件资源管理器可能会响应缓慢或崩溃。(Windows File Explorer)尝试清除文件资源管理器(File Explorer)历史记录并检查是否可以解决问题。
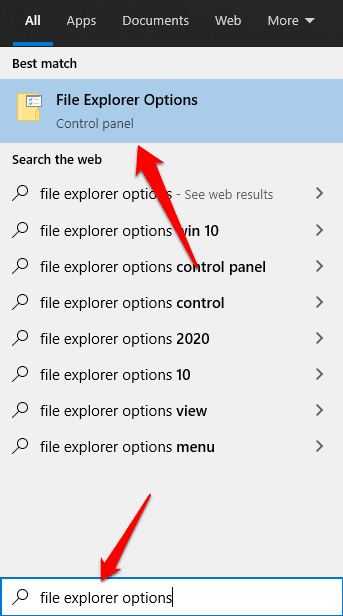
1.在Windows搜索栏中键入文件资源管理器选项,然后单击结果中的(file explorer options)文件资源管理器选项(File Explorer Options)。
2. 在“常规(General)”选项卡中,单击“清除文件资源管理器历史记录(Clear File Explorer History)”选项右侧的“清除(Clear)”按钮。您可以在“隐私(Privacy)”部分找到它。
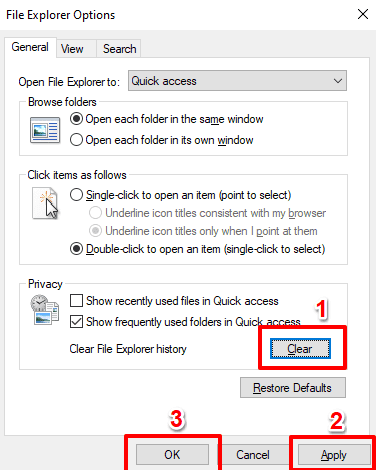
3. 单击应用(Apply),然后单击确定(OK)以保存更改。
文件资源管理器(File Explorer)现在应该在您重新启动时稳定且正常运行。否则,继续下一个解决方案。
5. 更新您 PC 的视频驱动程序
根据Microsoft 支持(Microsoft Support),如果您的 PC 的视频驱动程序损坏或过时, Windows 资源管理器可能会停止工作。(Windows Explorer)如果由于Windows 文件资源管理器(Windows File Explorer)没有响应而仍然无法浏览文件和文件夹,请尝试为您的 PC 下载并安装最新的视频驱动程序更新。将您的计算机连接到互联网并按照以下步骤操作。
右键单击开始或 Windows 图标(Start or Windows icon)并选择设备管理器(Device Manager)。

展开显示适配器(Display adapters)类别,右键单击 PC 的视频/图形适配器,然后选择更新驱动程序(Update driver)。

选择自动搜索更新的驱动程序软件(Search automatically for updated driver software)。

这将提示Windows在 Internet 和您的计算机上搜索适用于您 PC 的最新视频驱动程序。
6. 更新您 PC 的操作系统
(File Explorer)如果您的 Windows 10 版本过时,文件资源管理器可能会崩溃并且无法响应。下载(Download)并安装任何可用的更新并检查是否可以解决问题。
Windows更新通常附带安全补丁、驱动程序更新、错误修复以及影响Windows应用程序和进程的其他功能问题的解决方案。如果设备管理器(Device Manager)没有找到视频驱动程序的更新,请考虑更新您的 PC 操作系统。
转到设置(Settings )>更新和安全( Update & Security )> Windows 更新( Windows Update),然后单击检查更新(Check for updates)。

7. 扫描您的 PC 以查找病毒(Viruses)和恶意软件(Malware)
如果您的 PC 上安装了防病毒或反恶意软件,请对隐藏的病毒和恶意软件进行彻底扫描。请参阅本指南,了解如何使用(learn how to completely remove stubborn malware)Malwarebytes等受信任的软件从您的 PC中彻底删除顽固的恶意软件。
您还可以使用Windows内置的防病毒工具Windows Defender来清除恶意软件和病毒(nuke malware and viruses)。
8. 检查内存问题
如果随机存取存储器(Random Access Memory)出现问题,您的 PC 上的多个应用程序可能会出现故障。运行Windows 内存诊断(Windows Memory Diagnostics)工具来检查您的计算机是否存在内存问题(check your computer for memory problems)。确保在继续之前保存您的工作并关闭所有打开的应用程序。
1.在Windows搜索栏中键入内存,然后在结果中选择(memory)Windows 内存诊断(Windows Memory Diagnostic)。

2.两者会给你两个选择。选择“立即重新启动并检查问题(推荐)(Restart now and check for problems (recommended)) ”选项。

Windows 内存诊断程序(Windows Memory Diagnostics)将扫描您的 PC 并修复它发现的任何与内存相关的问题。
9. 执行系统还原
(Did)文件资源管理器(File Explorer)是否在安装应用程序、驱动程序、软件更新或更改某些系统配置后启动?尝试将您的 PC 回滚到以前的配置(或还原点)。
请注意,恢复到以前的还原点会更改一些系统设置。最近安装的程序和驱动程序也将从您的 PC 中删除。请按照以下步骤回滚到还原点。
1.在Windows搜索栏中键入控制面板,然后单击结果中的(control panel)控制面板(Control Panel)。
2. 点击恢复(Recovery)。

3. 选择打开系统还原(Open System Restore)。

4. 在系统还原(System Restore)窗口中,单击下一步(Next)继续。

5.最新/最新的系统还原点将出现在列表中。选择它并单击下一步(Next)继续。
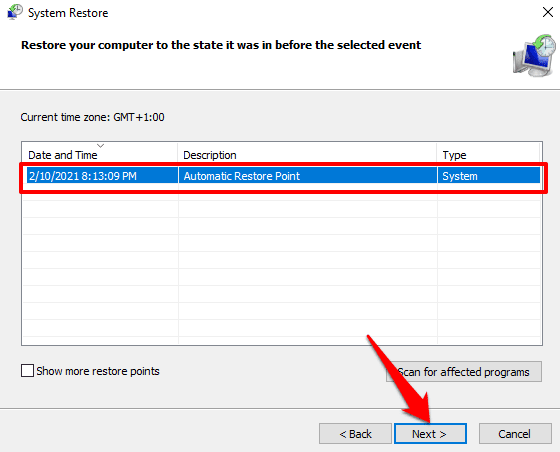
选中“显示更多还原点(Show more restore points)”选项以显示其他(较旧的)还原点。
6. 单击完成(Finish)开始系统恢复。

如果您没有找到还原点,那可能是因为您的计算机上的系统还原(System Restore)功能未激活。了解如何在 Windows(how to enable or disable System Restore on Windows)设备上启用或禁用系统还原。
让文件资源管理器再次工作
我们非常有信心,上面列出的至少一种故障排除方法应该可以解决Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)没有响应的问题。如果问题仍然存在,以安全模式重新启动 PC或执行干净启动应该会有所帮助。
How to Fix Windows 10 File Explorer Not Responding
File Explorer is the default file manаgement tool on Windows devices. Like every other system processes on Windows, File Explorer also has іts occasional moments of failure. If you find Windows Explorer not responding during usage, there are a fеw things you can try.
We’ve written a comprehensive guide covering tips to follow when Windows Explorer keeps crashing. In this article, we’ll rump through nine fixes to try when you launch the File Explorer and it keeps loading or fails to open files and folders.

1. Modify Your PC’s Display Layout
This is a rather bizarre but effective solution to Windows Explorer not responding. Apparently, using an unrecommended screen layout and resolution could cause the File Explorer to malfunction.
Check your PC’s display settings and make sure you’re using the recommended scale/layout. Go to Settings > System > Display and ensure the size of text, apps, and other items is set to 100% or whatever option Windows recommends.

If your PC’s display scaling is already set to 100%, try changing it to 125% and back to 100% again.
2. Kill and Restart the File Explorer
If Windows Explorer is still not responding after changing your PC’s resolution, terminate the Windows Explorer process and start it again. There are several ways to restart Windows Explorer:
Using Task Manager
Launch the Windows Task Manager (press Ctrl + Shift + Esc), right-click on Windows Explorer in the Apps section, and click End Task to terminate File Explorer.

Restart the Windows Explorer by clicking the folder icon in the taskbar. Alternatively, use the Task Manager: click on File on the menu bar and select Run new task.

Type explorer.exe in the dialog box and click OK.

That will start Windows Explorer immediately. Now proceed to check if you can access your files and folders in File Explorer without any lag.
Using Command Prompt
You can also use the Command Prompt utility to terminate and reinitiate the Windows Explorer. Right-click on the Windows icon and select Command Prompt (Admin) from the Quick Access menu. Input taskkill /f /im explorer.exe in the console and press Enter.

Your PC’s taskbar and desktop icons will disappear when you terminate the Windows Explorer. That’s normal and only temporary. To restart the File Explorer, input start explorer.exe in the Command Prompt window and press Enter to proceed.

Restart File Explorer Using A BAT File
BAT files let you easily automate tasks and actions. If File Explorer fails to respond quite often and restarting the process usually resolves the problem, you should create a BAT file dedicated to restarting the File Explorer at the click of a button.
- Right-click on an empty space on the desktop. Click New and then select Text Document.

- Name the document Restart Explorer and press Enter.

- Double-click on the newly-created file to open with Notepad.
- Paste the command below in the document:
taskkill /f /IM explorer.exe
start explorer.exe
exit

- Click on File in the menu bar and select Save As.

- In the FIle name dialog box, rename the file Restart Explorer.bat and make sure the Save as type option is set to All Files.

- Click Save to proceed.
To use the newly created BAT file to restart the Windows Explorer, return to the Desktop, right-click on the file, and select Run as administrator.

Windows will run the command in the BAT file through Command Prompt and restart the Windows Explorer.
3. Check for Corrupt System Files
When some system files get damaged, missing, or corrupt, some core Windows functionalities (like the File Explorer) may begin to malfunction. Thankfully, this is easy to fix. The System File Checker will scan your PC for corrupt or missing system files and fix or replace them accordingly.
Follow the steps below to run the System File Checker on your Windows 10 computer.
1. Right-click on the Start menu icon and select Command Prompt (Admin).

2. Type or paste the command below in the Command Prompt console and press Enter.
sfc /scannow

If the Windows File Explorer is still not responding when Command Prompt is done executing the command, restart your computer and try again.
4. Clear File Explorer History
The Windows File Explorer keeps a log of all previous actions and activities—recently accessed files and folders, searches, address bar entries, etc. The Windows File Explorer may respond slowly or crash when the utility’s history accumulates to a certain point. Try clearing the File Explorer history and check if that fixes the problem.
1. Type file explorer options in the Windows search bar and click File Explorer Options in the results.

2. In the General tab, click the Clear button to the right of the option that reads Clear File Explorer History. You’ll find that in the Privacy section.

3. Click Apply and then OK to save the changes.
File Explorer should now be stable and functional when you relaunch it. Otherwise, proceed to the next solution.
5. Update Your PC’s Video Driver
According to Microsoft Support, the Windows Explorer could stop working if your PC’s video driver is corrupt or outdated. If you still can’t navigate your files and folders because the Windows File Explorer is not responding, try downloading and installing the latest video driver update for your PC. Connect your computer to the internet and follow the steps below.
Right-click the Start or Windows icon and select Device Manager.

Expand the Display adapters category, right-click on your PC’s video/graphic adapter, and select Update driver.

Choose Search automatically for updated driver software.

That will prompt Windows to search the internet and your computer for the latest video driver for your PC.
6. Update Your PC’s Operating System
File Explorer may crash and fail to respond if your Windows 10 version is out-of-date. Download and install any available updates and check if that resolves the issue.
Windows updates often ship with security patches, driver updates, bug fixes, and solutions to other functional issues affecting Windows applications and processes. If the Device Manager doesn’t find an update for the video driver, consider updating your PC’s operating system.
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and click on the Check for updates.

7. Scan Your PC for Viruses and Malware
If you have an antivirus or antimalware software installed on your PC, run a thorough scan for hidden viruses and malware. Refer to this guide to learn how to completely remove stubborn malware from your PC using trusted software like Malwarebytes.
You can also use Windows built-in antivirus tool, Windows Defender, to nuke malware and viruses.
8. Check for Memory Problems
Several applications may malfunction on your PC if there’s a problem with the Random Access Memory. Run the Windows Memory Diagnostics tool to check your computer for memory problems. Make sure you save your work and close any open applications before you proceed.
1. Type memory in the Windows search bar and select Windows Memory Diagnostic in the result.

2. The two will present you with two options. Select the option that reads “Restart now and check for problems (recommended).”

The Windows Memory Diagnostics will scan your PC and fix any memory-related issues that it finds.
9. Perform a System Restore
Did the File Explorer start after installing an app, a driver, software update, or after changing certain system configurations? Try rolling your PC back to a previous configuration (or restore point).
Note that reverting to a previous restore point will change some system settings. Recently-installed programs and drivers will also be deleted from your PC. Follow the steps below to roll back to a restore point.
1. Type control panel in the Windows search bar and click Control Panel on the results.

2. Click on Recovery.

3. Select Open System Restore.

4. In the System Restore window, click Next to proceed.

5. The latest/newest system restore point will appear on the list. Select it and click Next to proceed.

Check the ‘Show more restore points’ option to reveal other (older) restore points.
6. Click Finish to commence the system restoration.

If you don’t find a restore point, that’s probably because the System Restore feature isn’t active on your computer. Learn how to enable or disable System Restore on Windows devices.
Get the File Explorer Working Again
We’re pretty confident that at least one of the troubleshooting methods listed above should resolve issues with Windows Explorer not responding. If the problem persists, restarting your PC in Safe Mode or performing a clean boot should help.





























