微软自成立以来,在更新其(Microsoft)Windows操作系统方面一直非常一致。他们定期向全球用户推送各种类型的更新(功能包更新、服务包更新、定义更新、安全更新、工具更新等)。这些更新包括对用户在当前操作系统构建中不幸遇到的许多错误和问题的修复,以及提高整体性能和用户体验的新功能。
但是,虽然新的操作系统更新可能会解决问题,但它也可能会提示出现其他一些问题。去年的Windows 10 1903更新因引发的问题多于解决的问题而臭名昭著。一些用户报告说,1903 更新导致他们的 CPU 使用率猛增 30%,在某些情况下甚至达到 100%。这使得他们的个人电脑速度慢得令人沮丧,并让他们拔出头发。更新后可能出现的其他一些常见问题是极端系统冻结、启动时间延长、鼠标点击和按键无响应、蓝屏死机等。
在本文中,我们将为您提供 8 种不同的解决方案,以提高您的计算机性能并使其像安装最新 Windows 10 更新之前一样快速。

修复 Windows 10 更新后运行缓慢的问题(Fix Windows 10 running slow after update problem)
如果当前更新未正确安装或与您的系统不兼容,您的 Windows 10 计算机可能运行缓慢。有时,新的更新可能会损坏一组设备驱动程序或导致系统文件损坏,从而导致性能下降。最后,更新本身可能充满了错误,在这种情况下,您将不得不回滚到以前的版本或等待Microsoft发布新版本。
Windows 10运行缓慢的 其他常见解决方案包括禁用影响较大的启动程序、限制应用程序在后台运行( restricting applications from running in the background )、更新所有设备驱动程序、卸载膨胀软件和恶意软件、修复损坏的系统文件等。
方法1:寻找任何新的更新
如前所述,Microsoft会定期发布新的更新来修复以前的问题。如果性能问题是更新的固有问题,那么微软(Microsoft)很可能已经意识到并且很可能已经为它发布了补丁。因此,在我们转向更持久和冗长的解决方案之前,请检查是否有任何新的Windows更新。
1. 按Windows键调出开始菜单,然后单击齿轮图标打开Windows 设置(Windows Settings) (或使用热键组合 Windows key + I)。

2. 点击更新和安全(Update & Security)。

3. 在Windows 更新(Windows Update)页面上,单击检查更新(Check for Updates)。

4. 如果确实有新的更新可用,请尽快下载并安装它以修复您的计算机性能。
方法 2:禁用启动(Startup)和后台应用程序(Background Applications)
我们所有人都安装了一堆我们几乎不使用的第三方应用程序,但仍然保留它们以备不时之需。其中一些可能有权在您的计算机每次启动时自动启动,因此会增加整体启动时间。除了这些第三方应用程序之外,微软(Microsoft)还捆绑了一长串允许始终在后台运行的本机应用程序。限制这些后台应用程序(Restricting these background apps)并禁用影响大的启动程序可以帮助释放一些有用的系统资源。
1. 右键单击屏幕底部的任务栏,然后 从随后出现的上下文菜单中 选择任务管理器(或按键盘上的(Task Manager)Ctrl + Shift + Esc)。
2. 切换到任务管理器窗口的启动 选项卡。(Startup )
3. 检查启动影响(Startup impact)列,查看哪个程序使用的资源最多,因此对您的启动时间影响很大。如果您发现您不经常使用的应用程序,请考虑禁用它在启动时自动启动。
4. 为此, 右键单击 (right-click )应用程序并选择 禁用 (Disable )(或单击右下角的禁用(Disable)按钮)。

要禁用本机应用程序在后台保持活动状态:
1. 打开 Windows设置 (Settings )并点击 隐私(Privacy)。

2. 在左侧面板中,单击后台应用程序(Background apps)。

3.关闭“让应用程序在后台运行”(Toggle off ‘Let apps run in the background’)以禁用所有后台应用程序或继续单独选择哪些应用程序可以在后台继续运行,哪些不能。
4.重新启动您的PC,看看您是否能够修复更新问题后运行缓慢的Windows 10。 ( fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem. )
方法 3:执行干净启动
如果特定应用程序导致您的计算机运行缓慢,您可以通过执行干净启动(performing a clean boot)来查明它。启动干净启动时,操作系统仅加载基本驱动程序和默认应用程序。这有助于避免由于第三方应用程序导致的可能导致性能低下的任何软件冲突。
1. 我们需要打开系统配置(System Configuration)应用程序来执行干净启动。要打开它, 请在运行命令框(Windows key + Rmsconfig ,然后按 Enter。

2. 在常规选项卡下,通过单击旁边的单选按钮启用选择性启动。(Selective startup)
3.启用选择性启动后,其下方的选项也将解锁。选中加载系统服务旁边的框。( Check the box next to Load system services.)确保禁用加载(Load)启动项选项(未选中)。

4. 现在,移至服务 选项卡并勾选(Services )隐藏所有 Microsoft 服务(Hide all Microsoft services)旁边的框 。接下来,单击 全部禁用(Disable all)。通过这样做,您终止了在后台运行的所有第三方进程和服务。

5. 最后,单击Apply 然后 单击OK 保存更改,然后 单击Restart。
另请阅读:(Also Read:) 修复无法下载 Windows 10 创意者更新(Fix Unable To Download Windows 10 Creators Update)
方法 4:删除不需要(Remove Unwanted)的和恶意软件(Malware)应用程序
除了第三方和本机应用程序之外,恶意软件的设计目的是占用系统资源并损坏您的计算机。他们因在没有提醒用户的情况下找到进入计算机的方式而臭名昭著。从 Internet 安装应用程序时应格外小心,并避免使用不受信任/未经验证的来源(大多数恶意软件程序与其他应用程序捆绑在一起)。此外,执行定期扫描以阻止这些需要大量内存的程序。
1. 在Cortana搜索栏中输入Windows 安全( (Windows security)Windows键 + S),然后按 Enter 打开内置安全应用程序并扫描恶意软件。

2. 单击左侧面板中的病毒和威胁防护(Virus & threat protection)。

3. 现在,您可以通过 从“扫描”选项中选择(Scan)“全面扫描”来运行(Full Scan)快速扫描(Quick Scan) 或对恶意软件进行更彻底的扫描 (或者,如果您有第三方防病毒或反恶意软件程序,如Malwarebytes,请通过它们运行扫描(Malwarebytes, run a scan through them))。
方法 5:更新所有驱动程序
Windows 更新因弄乱硬件驱动程序并导致它们变得不兼容而臭名昭著。通常,是显卡驱动程序变得不兼容/过时并提示性能问题。要解决任何与驱动程序相关的问题,请通过设备管理器将过时的驱动程序替换为最新的驱动程序。(replace the outdated drivers with the latest ones)

Driver Booster是最流行的Windows驱动程序更新应用程序。前往他们的官方网站并下载安装文件。下载后,单击.exe文件以启动安装向导并按照屏幕上的所有提示安装应用程序。打开驱动程序应用程序,然后单击立即扫描( Scan)。
等待(Wait)扫描过程完成,然后单独单击每个驱动程序旁边的更新驱动程序按钮或(Update Drivers)全部更新(Update All)按钮(您需要付费版本才能通过单击更新所有驱动程序)。
方法 6:修复损坏的系统文件(Repair Corrupt System Files)
安装不当的更新也可能最终破坏重要的系统文件并降低计算机速度。系统文件被渲染损坏或完全丢失是功能更新的常见问题,并在打开应用程序时导致各种错误、蓝屏死机、完全系统故障等。
要修复损坏的系统文件,您可以回滚到以前的Windows版本或运行 SFC 扫描。后者在下面解释(前者是此列表中的最终解决方案)。
1. 在Windows搜索栏中搜索(Windows)命令提示符(Command Prompt),在搜索结果上单击鼠标右键,然后选择以 管理员身份运行(Run As Administrator)。

您将收到一个用户帐户控制(User Account Control)弹出窗口,请求您允许命令提示符(Command Prompt)对您的系统进行更改。单击(Click)“ 是” (Yes )授予权限。
2.打开命令提示符(Command Prompt)窗口后,仔细键入以下命令并按 Enter 键执行。
sfc /scannow

3. 扫描过程需要一些时间,所以请坐下来,让命令提示符(Command Prompt)完成它的工作。如果扫描没有发现任何损坏的系统文件,那么您将看到以下文本:
Windows 资源保护未发现任何完整性违规。(Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.)
4.如果您的计算机在运行 SFC 扫描后仍然运行缓慢,请执行以下命令(修复Windows 10映像)。(Windows 10)
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

5. 命令完成处理后,重新启动 PC 并查看是否能够修复更新问题后运行缓慢的 Windows 10。 ( fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem. )
另请阅读:(Also Read:) 为什么 Windows 10 更新速度极慢?(Why are Windows 10 Updates Extremely Slow?)
方法 7:修改页面文件(Modify Pagefile)大小并禁用视觉(Disable Visual)效果
大多数用户可能没有意识到这一点,但除了RAM和硬盘驱动器之外,还有另一种类型的内存决定了计算机的性能。这种额外的内存称为分页文件(File),是每个硬盘上的虚拟内存。它作为 RAM 的扩展,当您的系统(RAM)RAM运行不足时,您的计算机会自动将一些数据传输到页面文件。页面文件还存储最近未访问的临时数据。
由于它是一种虚拟内存,您可以手动调整其值并欺骗您的计算机,使其相信有更多可用空间。除了增加分页(Paging)文件大小外,您还可以考虑禁用视觉效果以获得更清晰的体验(尽管美观会下降)。这两项调整都可以通过“性能(Performance) 选项(Options)”窗口进行。
1.在运行(Run)命令框中键入控制或控制面板( (Control Panel)Windows键 + R),然后按回车键打开应用程序。

2. 点击系统(System)。要更轻松地查找项目,请通过单击右上角的查看方式选项将图标大小更改为大或小。

3. 在以下系统属性(Properties)窗口中,单击 左侧的高级系统设置。(Advanced system settings)

4. 单击性能下的设置...(Settings…) 按钮。
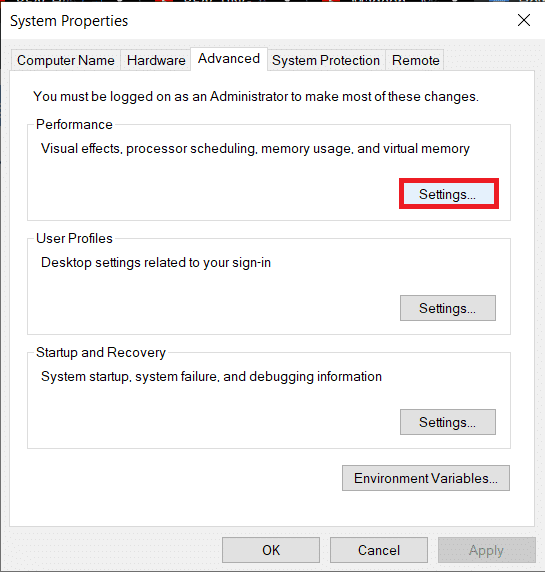
5. 切换到性能(Performance)选项窗口的(Options)高级 (Advanced )选项卡,然后单击 更改...(Change…)
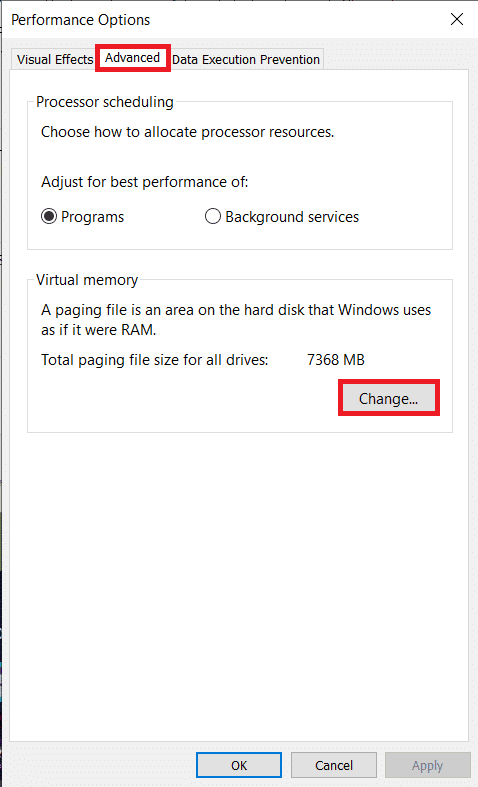
6.取消 选中(Untick )“自动管理所有驱动器的页面文件大小”(‘Automatically manage paging file size for all drives’)旁边的框 。
7. 选择您安装Windows的驱动器(通常是 C 驱动器),然后单击(Windows)自定义大小(Custom size)旁边的单选按钮。
8. 根据经验,初始大小(Initial size) 应等于 系统内存 (RAM) 的一倍半,(one and a half times of the system memory (RAM)) 最大 大小(Maximum size) 应为 初始大小的三倍(three times the initial size)。

例如:(For example:)如果您的计算机上有 8GB 的系统内存,那么初始(Initial)大小应该是 1.5 * 8192 MB (8 GB = 8 * 1024 MB) = 12288 MB,因此,最大(Maximum)大小应该是 12288 * 3 = 36864兆。
9. 在初始(Initial)和最大(Maximum)尺寸旁边的框中输入值后,单击设置(Set)。
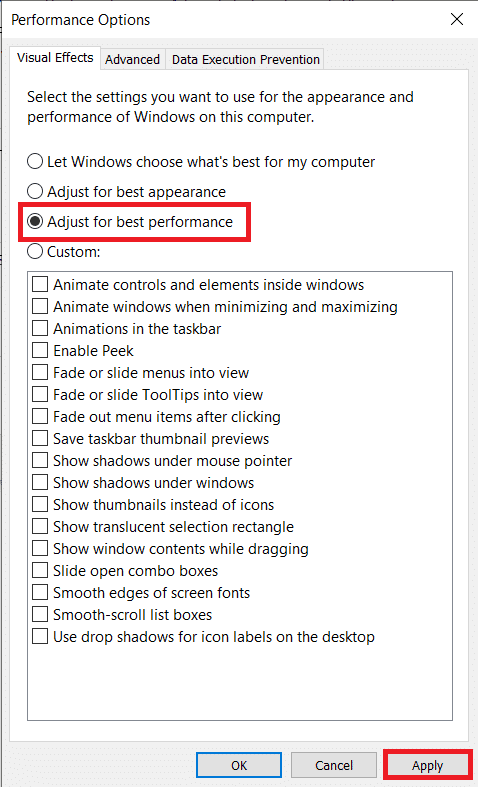
10. 当我们打开性能(Performance) 选项(Options)窗口时,让我们也禁用所有视觉效果/动画。
11. 在视觉效果选项卡下,启用调整以获得最佳性能 (enable Adjust for best performance )以禁用所有效果。最后点击 确定 (OK )保存退出。
方法8:卸载新更新
最后,如果上述解决方案都不能帮助您提高计算机的性能,那么您最好卸载当前的更新并回滚到没有您当前遇到的任何问题的先前版本。你可以随时等待微软(Microsoft)在未来发布更好、更麻烦的更新。
1.按Windows键 + I打开 Windows设置 (Settings ),然后单击 更新和安全(Update & Security)。
2.在右侧面板上向下滚动(Scroll)并单击查看更新历史记录(View update history)。

3. 接下来,单击卸载更新(Uninstall updates) 超链接。
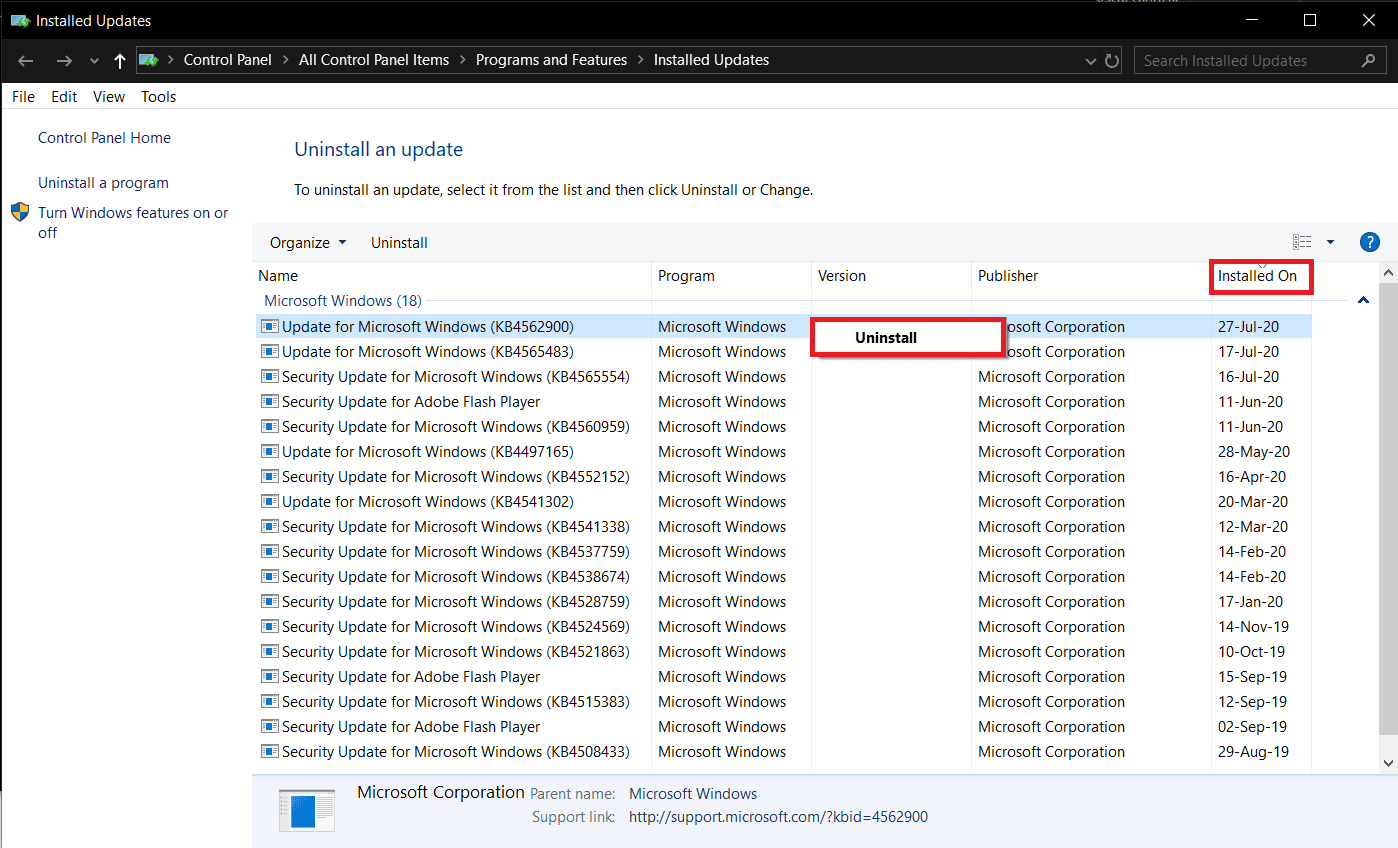
4. 在以下窗口中,单击Installed On标题以根据安装日期对所有功能和安全操作系统更新进行排序。
5.右键单击 (Right-click )最近安装的更新并选择 卸载(Uninstall)。按照屏幕上的说明进行操作。
受到推崇的:(Recommended:)
在下面的评论中让我们知道上述哪种方法可以恢复您的 Windows 10 计算机的性能。此外,如果您的计算机继续运行缓慢,请考虑从HDD升级到SSD(查看SSD 与 HDD:哪个更好(SSD Vs HDD: Which one is better))或尝试增加RAM量。
How to Fix Windows 10 running slow after update
Microsoft, since its inception, has been pretty consistent when it comeѕ to updating its Windows operating system. Τhey regularly push various types of updates (featυre pack update, service pack update, defіnition uрdatе, securitу update, tool updаtes, etc.) to their userѕ acrоss the globe. These updates include fixes for a number of bugs and іssues that users are unfortunately encountering on the current OS build along with new features to boоst the overall performance and user experience.
However, while a new OS update may solve an issue, it can also prompt another few to appear. The Windows 10 1903 update of yesteryear was infamous for causing more problems than it solved. Some users reported that the 1903 update caused their CPU usage to shoot up by 30 percent and in some situations, by 100 percent. This made their personal computers frustratingly slow and had them pulling their hair out. A few other common issues that may occur after updating are extreme system freezes, prolonged startup times, unresponsive mouse clicks and key presses, blue screen of death, etc.
In this article, we will be providing you with 8 different solutions to improve your computer’s performance and make it as snappier as it was before you installed the latest Windows 10 update.

Fix Windows 10 running slow after update problem
Your Windows 10 computer may be running slow if the current update hasn’t been installed properly or is incompatible with your system. Sometimes a new update can damage a set of device drivers or render system files corrupt prompting low performance. Lastly, the update itself may be full of bugs in which case you will have to roll back to the previous build or wait for Microsoft to release a new one.
Other common solutions for Windows 10 running slow include disabling high-impact startup programs, restricting applications from running in the background , updating all device drivers, uninstalling bloatware and malware, repairing corrupt system files, etc.
Method 1: Look for any new update
As mentioned earlier, Microsoft regularly releases new updates fixing issues in the previous ones. If the performance issue is an inherent problem with an update, then chances are Microsoft is already aware and has most likely released a patch for it. So before we move onto the more permanent and lengthy solutions, check for any new Windows updates.
1. Press the Windows key to bring up the start menu and click on the cogwheel icon to open Windows Settings (or use the hotkey combination Windows key + I).

2. Click on Update & Security.

3. On the Windows Update page, click on Check for Updates.

4. If a new update is indeed available, download and install it as soon as possible to fix your computer’s performance.
Method 2: Disable Startup & Background Applications
All of us have a bunch of third-party applications installed that we barely use, but keep them nevertheless for when a rare opportunity arises. Some of these may have the permission to start automatically every time your computer boots up and as a result, increase the overall startup time. Along with these third-party applications, Microsoft bundles in a long list of native applications that are allowed to always run in the background. Restricting these background apps and disabling high-impact startup programs can help free up some useful system resources.
1. Right-click on the taskbar at the bottom of your screen and select Task Manager from the ensuing context menu (or press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard).

2. Switch to the Startup tab of the Task Manager window.
3. Check the Startup impact column to see which program utilizes the most resources and therefore, has a high impact on your startup time. If you find an application that you do not use frequently, consider disabling it from launching automatically at startup.
4. To do so, right-click on an application and select Disable (or click on the Disable button at the bottom-right).

To disable native applications from staying active in the background:
1. Open Windows Settings and click on Privacy.

2. From the left panel, click on Background apps.

3. Toggle off ‘Let apps run in the background’ to disable all background applications or go ahead and individually select which apps can continue running in the background & which ones can’t.
4. Restart your PC and see if you’re able to fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem.
Method 3: Perform a Clean Boot
If a specific application is causing your computer to run slow, you can pinpoint it by performing a clean boot. When you initiate a clean boot, the OS loads only the essential drivers and default applications. This helps avoid any software conflicts caused due to third-party applications that might be prompting low performance.
1. We will need to open the System Configuration application to perform a clean boot. To open it, type msconfig in either the Run command box (Windows key + R) or the search bar and press enter.

2. Under the General tab, enable Selective startup by clicking on the radio button next to it.
3. Once you enable Selective startup, the options underneath it will also unlock. Check the box next to Load system services. Ensure the Load startup items option is disabled (unticked).

4. Now, move over to the Services tab and tick the box next to Hide all Microsoft services. Next, click Disable all. By doing this, you terminated all third-party processes and services that were running in the background.

5. Finally, click on Apply followed by OK to save the changes and then Restart.
Also Read: Fix Unable To Download Windows 10 Creators Update
Method 4: Remove Unwanted and Malware applications
Third-party and native applications aside, malicious software is purposely designed to hog up system resources and damage your computer. They are notorious for finding their way onto computers without ever alerting the user. One should be extremely cautious when installing applications from the internet and avoid untrusted/unverified sources (most malware programs are bundled with other applications). Also, perform regular scans to keep these memory-hungry programs at bay.
1. Type Windows security in the Cortana search bar (Windows key + S) and press enter to open the built-in security application and scan for malware.

2. Click on Virus & threat protection in the left panel.

3. Now, you can either run a Quick Scan or run a more thorough scan for malware by choosing Full Scan from Scan options (or if you have a third-party antivirus or antimalware program like Malwarebytes, run a scan through them).
Method 5: Update All Drivers
Windows updates are infamous for messing up hardware drivers and causing them to become incompatible. Usually, it is the graphic card drivers that become incompatible/outdated and prompt performance issues. To resolve any driver-related problem, replace the outdated drivers with the latest ones via the Device Manager.

Driver Booster is the most popular driver updating applications for Windows. Head over to their official websites and download the installation file. Once downloaded, click on the .exe file to launch the installation wizard and follow all the on-screen prompts to install the application. Open the driver application and click on Scan Now.
Wait for the scanning process to complete and then individually click on the Update Drivers button next to each driver or the Update All button (you will require the paid version to update all drivers with a single click).
Method 6: Repair Corrupt System Files
A poorly installed update can also end up breaking important system files and slow down your computer. System files being rendered corrupt or going missing altogether is a common issue with feature updates and leads to a variety of errors when opening apps, blue screen of death, a complete system failure, etc.
To repair corrupt system files, you can either roll back to the previous Windows version or run an SFC scan. The latter of which is explained below (the former is the final solution in this list).
1. Search for Command Prompt in the Windows search bar, right-click on the search result, and select Run As Administrator.

You will receive a User Account Control pop-up requesting your permission to allow Command Prompt to make changes to your system. Click on Yes to grant permission.
2. Once the Command Prompt window opens up, carefully type the following command and press enter to execute.
sfc /scannow

3. The scanning process will take some time so sit back and let the Command Prompt do its thing. If the scan didn’t find any corrupt system files, then you will see the following text:
Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.
4. Execute the below command (to repair Windows 10 image) if your computer continues to run slow even after running an SFC scan.
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

5. Once the command finishes processing, reboot your PC and see if you’re able to fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem.
Also Read: Why are Windows 10 Updates Extremely Slow?
Method 7: Modify Pagefile size & Disable Visual Effects
Most users might be unaware of this, but along with your RAM and hard drive, there is another type of memory that dictates your computer’s performance. This additional memory is known as Paging File and is a virtual memory present on every hard disk. It serves as an extension to your RAM and your computer automatically transfers some data to the paging file when your system RAM is running low. The paging file also stores temporary data that hasn’t been accessed lately.
Since it is a type of virtual memory, you can manually adjust its values and fool your computer into believing that there is more space available. Along with increasing the Paging file size, you can also consider disabling the visual effects for a crispier experience (although the aesthetics will go down). Both these adjustments can be made through the Performance Options window.
1. Type Control or Control Panel in the Run command box (Windows key + R) and press enter to open the application.

2. Click on System. To make looking for the item easier, change the icon size to large or small by clicking on the View by option at the top-right.

3. In the following System Properties window, click on Advanced system settings on the left.

4. Click on the Settings… button under Performance.

5. Switch to the Advanced tab of the Performance Options window and click on Change…

6. Untick the box next to ‘Automatically manage paging file size for all drives’.
7. Select the drive on which you have installed Windows (normally the C drive) and click on the radio button next to Custom size.
8. As a rule of thumb, the Initial size should be equal to one and a half times of the system memory (RAM) and the Maximum size should be three times the initial size.

For example: If you have 8gb of system memory on your computer, then the Initial size should be 1.5 * 8192 MB (8 GB = 8 * 1024 MB) = 12288 MB, and consequently, the Maximum size would be 12288 * 3 = 36864 MB.
9. Once you have entered the values in the boxes next to Initial and Maximum size, click on Set.
10. While we have the Performance Options window open, let’s also disable all the visual effects/animations.
11. Under the Visual Effects tab, enable Adjust for best performance to disable all effects. Finally, click on OK to save and exit.

Method 8: Uninstall the new update
Ultimately, if none of the above solutions helped you improve your computer’s performance, it might be best for you to uninstall the current update and roll back to a previous build that didn’t have any of the issues you are currently experiencing. You can always wait for Microsoft to release a better and less troublesome update in the future.
1. Open Windows Settings by pressing Windows key + I and click on Update & Security.
2. Scroll down on the right panel and click on View update history.

3. Next, click on the Uninstall updates hyperlink.

4. In the following window, click on the Installed On header to sort all feature and security OS updates based on their installation dates.
5. Right-click on the most recently installed update and select Uninstall. Follow the on-screen instructions that follow.

Recommended:
Let us know which of the above methods revived the performance of your Windows 10 computer in the comments below. Also, if your computer continues to run slow, consider upgrading from an HDD to an SSD (Check out SSD Vs HDD: Which one is better) or try increasing the amount of RAM.



























